Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the following and mark the correct option
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Sternum | i. Synovial fluid |
| B. Glenoid Cavity | ii. Vertebrae |
| C. Freely movable joint | iii. Pectoral girdle |
| D. Cartilaginous joint | iv. Flat bones |
विकल्प
A - ii, B - i, C - iii, D - iv
A - iv, B - iii, C - i, D - ii
A - ii, B - i, C - iv, D - iii
A - iv, B - i, C - ii, D - iv
उत्तर
A - iv, B - iii, C - i, D - ii
Explanation:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Sternum | iv. Flat bones |
| B. Glenoid Cavity | iii. Pectoral girdle |
| C. Freely movable joint | i. Synovial fluid |
| D. Cartilaginous joint | ii. Vertebrae |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Alongside is shown a diagrammatic skeletal of synovial j oint.
(a) What is a synovial joint?
(b) Where do you find such a joint?
(c) What is the function of cartilages?
(d) Name the parts 1 to 5. 2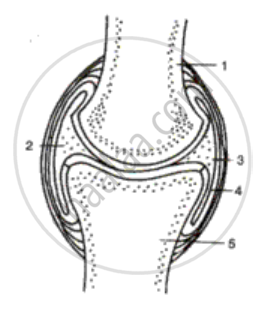
The ______ joint is seen in fingers and toes.
What will happen if there are no joints in our body?
Answer the following:
Why can our elbow not move backwards?
The greatest range of movement is seen in ______ joint.
There are ______ types of movable joints.
Flat bones are seen in ______.
Provide one-word answers to the statement given below
Joint which allows movement in all directions.
Unscramble the jumbled word and write them in the blank spaces provided.
iontcaronct
Name the type of joint between the following:
Femur/acetabulum
