Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name the device which converts the change in intensity of illumination to change in electric current flowing through it. Plot I-V characteristics of this device for different intensities. State any two applications of this device.
उत्तर
Photodiodes are used to detect optical signals of different intensities by changing current flowing through them.
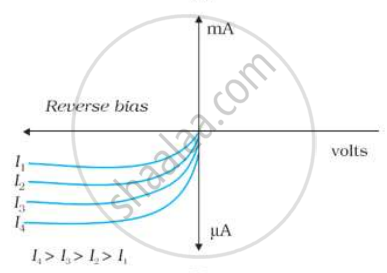
I-V Characteristics of a photodiode
Applications of photodiodes:
- In detection of optical signals.
- In demodulation of optical signals.
- In light operated switches.
- In speed reading of computer punched cards.
- In electronic counters.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the working of a photodiode.
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Forward biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
The width of depletion region of p-n junction diode is _______.
(A) 0.5 nm to 1 nm
(B) 5 nm to 10 nm
(C) 50 nm to 500 nm
(D) 500 nm to 1000 nm
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in reverse bias. Plot the V-I characteristics in this case.
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of the band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
What is a solar cell?
If the resistance R1 is increased (Figure), how will the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter change?
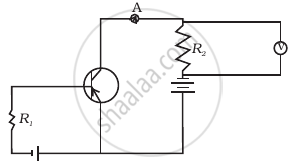
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
LED is a heavily doped P-N junction which under forward bias emits spontaneous radiation. When it is forward-biased, due to recombination of holes and electrons at the junction, energy is released in the form of photons. In the case of Si and Ge diode, the energy released in recombination lies in the infrared region. LEDs that can emit red, yellow, orange, green and blue light are commercially available. The semiconductor used for fabrication of visible LEDs must at least have a band gap of 1.8 eV. The compound semiconductor Gallium Arsenide – Phosphide is used for making LEDs of different colours.
|
- Why are LEDs made of compound semiconductor and not of elemental semiconductors?
- What should be the order of bandgap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
- A student connects the blue coloured LED as shown in the figure. The LED did not glow when switch S is closed. Explain why?
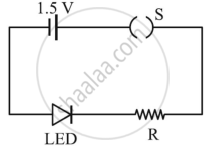
OR
iii. Draw V-I characteristic of a p-n junction diode in
(i) forward bias and (ii) reverse bias
Briefly explain how emf is generated in a solar cell.

