Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
On heating lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas “A”. The gas “A” on cooling changes to colourless solid “B”. Solid “B” on heating with NO changes to a blue solid ‘C’. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ and also write reactions involved and draw the structures of ‘B’ and ‘C’.
उत्तर
The gas A is \[\ce{NO2}\]. The reactions are explained as under:
\[\ce{2Pb(NO3)2 ->[Heat][673 K] + 2PbO + \underset{(Brown colour)}{\underset{Nitrogen dioxide}{\underset{(A)}{4NO2}}} + O2}\]
\[\ce{2NO2 ->[Cooling] \underset{Solid (Colourless)}{\underset{(B)}{N2O4}}}\]
\[\ce{2NO + N2O4 ->[Heating] \underset{Dinitrogen trioxide}{\underset{(C)}{\underset{Blue solid}{2N2O3}}}}\]
Structure of B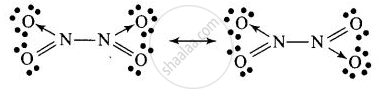
Structure of C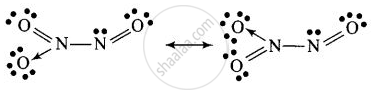
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write balanced chemical equations for action of potassium permanganate on: Hydrogen
Pb(NO3)2 on heating gives a brown gas which undergoes dimerisation on cooling? Identify the gas
Write balanced chemical equations for action of potassium permanganate on Warm conc. sulphuric acid
Which of the following statements is not correct for nitrogen?
Nitrogen is relatively inactive element because ____________.
Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is a coloured gas?
On heating lead nitrate forms oxides of nitrogen and lead. The oxides formed are ______.
Assertion: \[\ce{HNO3}\] makes iron passive.
Reason: \[\ce{HNO3}\] forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
HCl is added to following oxides. Which one would give H2O2
Assertion: Nitrogen and oxygen are the main components in. the atmosphere but these do not react to form oxides of nitrogen.
Reason: The reaction between nitrogen and oxygen requires high temperature.
