Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
On heating lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas “A”. The gas “A” on cooling changes to colourless solid “B”. Solid “B” on heating with NO changes to a blue solid ‘C’. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ and also write reactions involved and draw the structures of ‘B’ and ‘C’.
उत्तर
The gas A is \[\ce{NO2}\]. The reactions are explained as under:
\[\ce{2Pb(NO3)2 ->[Heat][673 K] + 2PbO + \underset{(Brown colour)}{\underset{Nitrogen dioxide}{\underset{(A)}{4NO2}}} + O2}\]
\[\ce{2NO2 ->[Cooling] \underset{Solid (Colourless)}{\underset{(B)}{N2O4}}}\]
\[\ce{2NO + N2O4 ->[Heating] \underset{Dinitrogen trioxide}{\underset{(C)}{\underset{Blue solid}{2N2O3}}}}\]
Structure of B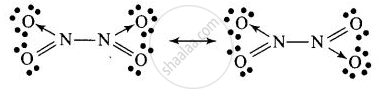
Structure of C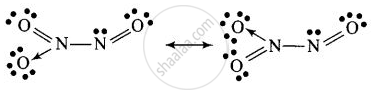
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why does NO2 dimerise?
Explain why Mn2+ ion is more stable than Mn3+? (Given : Mn→ Z=25)
Pick out the wrong statement.
Among the 15th group elements, as we move from nitrogen to bismuth, the pentavalency becomes less pronounced and trivalency becomes more pronounced due to:
Pure nitrogen is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of:
Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is a coloured gas?
Which of the following oxides of nitrogen reacts with FeSO4 to form a dark brown compound?
Assertion: \[\ce{HNO3}\] makes iron passive.
Reason: \[\ce{HNO3}\] forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
Which oxide of nitrogen is obtained on heating ammonium nitrate at 250°C?
Heating white phosphorus with conc. NaOH solution gives mainly ______.
