Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
On heating lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas “A”. The gas “A” on cooling changes to colourless solid “B”. Solid “B” on heating with NO changes to a blue solid ‘C’. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ and also write reactions involved and draw the structures of ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Solution
The gas A is \[\ce{NO2}\]. The reactions are explained as under:
\[\ce{2Pb(NO3)2 ->[Heat][673 K] + 2PbO + \underset{(Brown colour)}{\underset{Nitrogen dioxide}{\underset{(A)}{4NO2}}} + O2}\]
\[\ce{2NO2 ->[Cooling] \underset{Solid (Colourless)}{\underset{(B)}{N2O4}}}\]
\[\ce{2NO + N2O4 ->[Heating] \underset{Dinitrogen trioxide}{\underset{(C)}{\underset{Blue solid}{2N2O3}}}}\]
Structure of B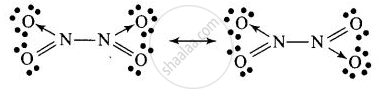
Structure of C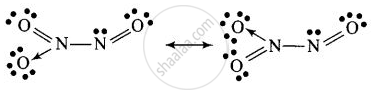
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write balanced chemical equations for action of potassium permanganate on: Hydrogen
Why does NO2 dimerise?
Tendency to show –3 oxidation state decrease from Nitrogn (N) to Bismuth (Bi).
Nitrogen is relatively inactive element because ____________.
The bonds present in N2O5 are ____________.
Which of the following oxides of nitrogen is a coloured gas?
In which one of the following oxides of nitrogen, one nitrogen atom is not directly linked to oxygen?
A deep brown gas is formed by mixing two colourless gases which are:
HCl is added to following oxides. Which one would give H2O2
Which oxide of nitrogen is obtained on heating ammonium nitrate at 250°C?
