Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Predict the product of the following reaction:
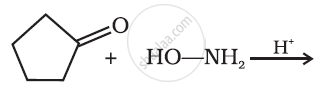
उत्तर

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Acetaldehyde, when treated with which among the following reagents does NOT undergo addition reaction?
(A) Ammonia
(B) Hydroxylamine
(C) Ammoniacal silver nitrate
(D) Semicarbazide
Write balanced chemical equations for action of ammonia on - formaldehyde
Arrange the following compound in increasing order of its reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
Benzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.
Hint: Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
Predict the product of the following reaction:
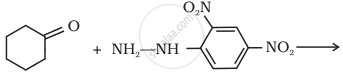
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Cyanohydrin
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Bromobenzene to 1-Phenylethanol
Explain the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide with energy profile diagram.
Write balanced chemical equations for action of ammonia on - acetone
Acetone, Acetaldehyde, Benzaldehyde, Acetophenone – reactivity towards addition of HCN.
Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
Reaction of aqueous sodium hydroxide on chlorobenzene gives which of the following products?
Write the name of product formed, when acetone is treated with 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine.
What happens when propanone is treated with CH3MgBr and then hydrolysed?
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| The carbon-oxygen double bond is polarised in aldehydes and ketones due to higher electronegativity of oxygen relative to carbon. Therefore, they undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with a number of nucleophiles such as HCN, NaHSO3, alcohols, ammonia derivatives and Grignard reagents. Aldehydes are easily oxidised by mild oxidising agents as compared to ketones. The carbonyl group of carboxylic acid does not give reactions of aldehydes and ketones. Carboxylic acids are considerably more acidic than alcohols and most of simple phenols. |
Answer the following:
(a) Write the name of the product when an aldehyde reacts with excess alcohol in the presence of dry HCl. (1)
(b) Why carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol? (1)
(c) (i) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity towards CH3MgBr: (1)
CH3CHO, \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{(CH3)3C-C-CH3}\\
\phantom{....}||\\
\phantom{....}\ce{O}
\end{array}\], \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-C-CH3}\\
||\\
\ce{O}
\end{array}\]
(ii) Write a chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone. (1)
OR
(c) Write the main product in the following: (2)
| (i) | 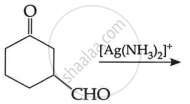 |
| (ii) | 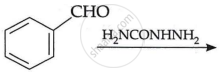 |
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxylamine to form ______.
Why dissociation of HCN is suppressed by the addition of HCL?
Draw structures of the following derivative.
The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
Draw structure of the following derivative.
The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
