Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide with energy profile diagram.
उत्तर
Mechanism of Alkaline hydrolysis of tert-alkyl halide.
Consider the action of aqueous sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide on a tertiary alkyl halide such as t-butyl bromide.
\[\ce{(CH3)3 CBr + KOH}\] \[\ce{(CH3)3 COH + KBr}\]
The ionic form of the reaction is:
\[\ce{(CH3)3 CBr + :\bar{O}H}\] \[\ce{(CH3)3 COH + Br^-}\]
During this hydrolysis the stronger nucleophile, :OH–
has displaced the weaker nucleophile, Br– and therefore, it is nucleophilic substitution (SN) reaction.
Kineties of reaction: Experimentally is observed that the rate of the reaction depends only on the concentration of (CH3)3CBr and is independent of the concentration of the OH– ions, i.e.,
Rate = k [(CH3)3CBr]
Therefore, this reaction is first order nucleophilic substitution reaction SN1 reaction.
Mechanism: This nuclephilic substitution takes place in two steps which can be represented as follows.
Step (i): Ionization of t-butyl bromide:

The three methyl groups of tert-butyl bromide sterically hinder the approach of the nucleophile and thus prevent the backside attack. Therefore in the first step C–Br bond ionizes to give t-butyl carbocation and bromide ion.
Due to gradual breaking of the bond a transition state (T.S)1 is formed. The electron repelling inductive effect of the methyl groups facilitates the ionization, by stabilising, carbocation.
Step (ii): Attack of nucleophile `( :barO H)`

The nucleophile `( : barO H)` attacks the carbocation forming t-butyl alcohol. But due to gradual formation of the C–OH bond a transition state (T.S)2 is first formed. The carbocation has planar configuration, hence it can be attacked by the nucleophile from either side. The frontside attack results in the product with retention of configuration. However, the backside attack results in the product with inversion of configuration. Since the attack from either side is equally probable, there will be retention in 50% of the molecules and inversion in the 50% of the molecules.
Energy profile diagram is obtained by plotting the potential energies of all the species against the reaction co-ordinates. The two-humps in the graph indicates two steps in the reaction.
Activation energy is the energy which must be supplied to reactants in order to form the transition state. It is equal to difference in potential energies of reactants and the transition state. The step-(i) has a higher activation energy, hence it is slow. The step-(ii) has lower activation energy, hence it is fast.

Ea1 = Energy of activation for step 1
Ea2 = Energy of activation for step 2
?H = Heat of reaction.
In multi-step reactions the slowest step determines the overall rate of reaction. This is called the rate controlling step. In the slow step only t-butyl bormide takes part and not the nucleophile. Hence it is a first order reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structures of the main products when acetone (CH3 − CO − CH3) reacts with the following reagent :
H2N − NHCONH2/H+
Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents : H2N – OH
Arrange the following compound in increasing order of its reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone.
Hint: Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
Predict the product of the following reaction:
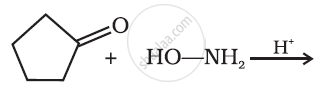
Predict the product of the following reaction:
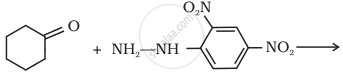
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Cyanohydrin
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
Semicarbazide and weak acid
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Bromobenzene to 1-Phenylethanol
Give plausible explanation for the following:
There are two −NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
Write balanced chemical equations for action of ammonia on - acetone
Write balanced chemical equations for action of ammonia on - acetone
How will you convert sodium acetate to methane?
Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
Alkenes 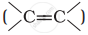 and carbonyl compounds
and carbonyl compounds 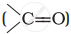 , both contain a π bond but alkenes show electrophilic addition reactions whereas carbonyl compounds show nucleophilic addition reactions. Explain.
, both contain a π bond but alkenes show electrophilic addition reactions whereas carbonyl compounds show nucleophilic addition reactions. Explain.
Which of the following has the most acidic hydrogen?
What happens when propanone is treated with CH3MgBr and then hydrolysed?
In the following reaction
\[\ce{Carbonyl compound + MeOH <=>[HCl] acetal}\]
Rate of the reaction is the highest for ______.
Which of the following is most reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions?
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxylamine to form ______.
Write the structure of the product formed when acetone reacts with 2, 4 DNP reagent.
Draw structures of the given derivatives.
The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
Draw the structure of the following derivative.
The ethylene ketal of hexane-3-one
Draw structure of the following derivative.
The ethylene ketal of hexane-3-one
Draw structure of the following derivative.
The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
Draw the structure of the following derivative.
Acetaldehydedimethylacetal
