Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Repeat Question 6, if `overline"AB"` happens to be a diameter.
उत्तर
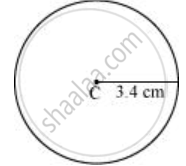
- Mark any point C on the sheet.
- By adjusting the compasses up to 3.4 cm and by putting the pointer of the compasses at point C, turn the compasses slowly to draw the circle. It is the required circle of 3.4 cm radius.
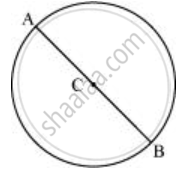
- Mark any diameter `overline"AB"` in the circle.
-
Now, taking A and B as centres, draw arcs on both sides of `overline"AB"` taking radius more than `overline"AB"`. Let these intersect each other at D and E.

- Join DE, which is the perpendicular bisector of AB.

It can be observed that `overline"DE"` is passing through the centre C of the circle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a line segment PQ = 4.8 cm. Construct the perpendicular bisector of PQ.
Draw a line segment AB = 6.2 cm. Mark a point P in AB such that BP = 4 cm. Through point P draw perpendicular to AB.
Draw a line segment AB of length 5.5 cm. Bisect it using a compass and ruler.
Draw the images of points A and B in line l of figure and name them as A’ and B’, respectively. Measure AB and A’B’. Are they equal?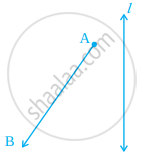
Draw a line segment of length 6.5 cm and divide it into four equal parts, using ruler and compasses.
Draw an angle of 140° with the help of a protractor and bisect it using ruler and compasses.
Draw an angle of 60° using ruler and compasses and divide it into four equal parts. Measure each part.
Draw a line segment of length 10 cm. Divide it into four equal parts. Measure each of these parts.
Draw the perpendicular bisector of `overline"XY"` whose length is 10.3 cm.
- Take any point P on the bisector drawn. Examine whether PX = PY
-
If M is the midpoint of `overline"XY"`, what can you say about the lengths MX and XY?
Draw a circle with centre C and radius 3.4 cm. Draw any chord `overline"AB"`. Construct the perpendicular bisector of `overline"AB"` and examine if it passes through C.
