Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Repeat Question 6, if `overline"AB"` happens to be a diameter.
उत्तर
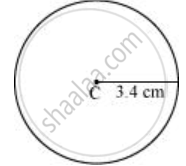
- Mark any point C on the sheet.
- By adjusting the compasses up to 3.4 cm and by putting the pointer of the compasses at point C, turn the compasses slowly to draw the circle. It is the required circle of 3.4 cm radius.
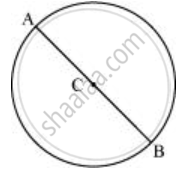
- Mark any diameter `overline"AB"` in the circle.
-
Now, taking A and B as centres, draw arcs on both sides of `overline"AB"` taking radius more than `overline"AB"`. Let these intersect each other at D and E.

- Join DE, which is the perpendicular bisector of AB.

It can be observed that `overline"DE"` is passing through the centre C of the circle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a line segment of given length and construct a perpendicular bisector to line segment using scale and compass
7 cm
Draw a line segment of given length and construct a perpendicular bisector to line segment using scale and compass
5.6 cm
Draw a line segment of given length and construct a perpendicular bisector to line segment using scale and compass
10.4 cm
Draw the images of points A and B in line l of figure and name them as A’ and B’, respectively. Measure AB and A’B’. Are they equal?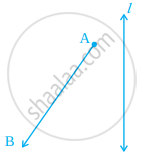
Bisect ∠XYZ of figure.
Bisect a right angle, using ruler and compasses. Measure each part. Bisect each of these parts. What will be the measure of each of these parts?
Draw a line segment of length 6 cm. Construct its perpendicular bisector. Measure the two parts of theline segment.
Draw a line segment of length 10 cm. Divide it into four equal parts. Measure each of these parts.
Draw `overline"AB"` of length 7.3 cm and find its axis of symmetry.
Draw a line segment of length 12.8 cm. Using compasses, divide it into four equal parts. Verify by actual measurement.
