Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Root hairs become flaccid, when fertilizers are added to the moist soil around it. Explain.
उत्तर
When fertilizers are added to the moist soil around it, it will form hypertonic solution, resulting the protoplasm to shrink and plasma membrane withdraw itself from the cell wall. Hence, the root hairs also become limp or flaccid.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Mention whether the following statement is true or false. Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
The cell wall of the root cell is a differentially permeable membrane.
The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate the following:
1. Strong sugar solution
2. Cell wall
3. Protoplasm
4. Large vacuole
5. Nucleus
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
(i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
(ii) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(iii) If the cell had been placed in distilled water instead of strong sugar solution which feature would not have been present?
(iv) If the cell in the diagram possessed chloroplasts where would these be present?
(v) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in animal cells.

The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
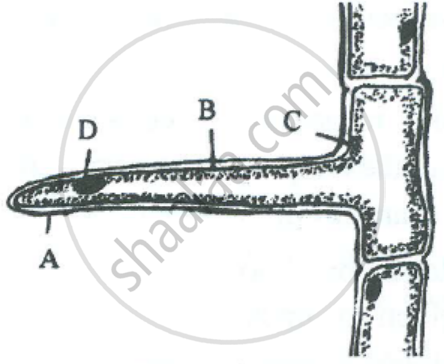
Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
Study the experimental setup in the figure and then answer the question that follow.
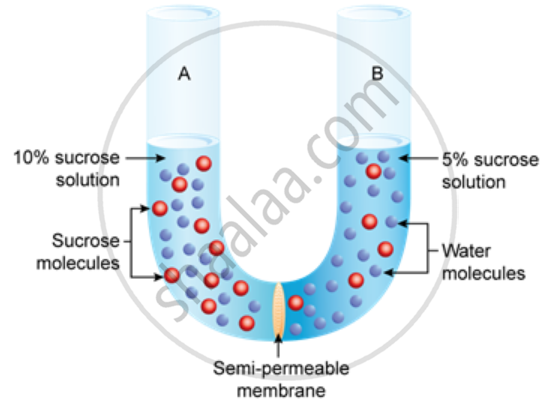
What will you observe in the setup after about half an hour? Give reasons for your answer.
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Diffusion | (a) The exit or flow of water from the cell to the outer environment. |
| (ii) Xylem | (b) The shrinkage of protoplasm when the cell is kept in a hypertonic solution. |
| (iii) Root pressure | (c) The tissue through which water and mineral salts move upward in a plant. |
| (iv) Isotonic solution | (d) Two solutions which have equal osmotic pressure. |
| (v) Exosmosis | (e) The process by which the molecules of perfume spread in the room when the bottle is open. |
| (vi) Osmosis | (f) The process by which roots absorb water from the soil. |
| (vii) Plasmolysis | (g) The pressure by which water rises up to some feet in a lofty tree. |
| (viii) Hypotonic solution | (h) The concentration of the solution when lower than that of the cell sap. |
A thin strip of epidermal cells of a leaf was observed in a drop of water. They all looked turgid and normal.
(a) Draw a diagram of such a cell.
(b) Draw a diagram of a cell if this strip is transferred to a strong concentrated solution of sugar. What is term used for the effect on the cells ?
What is the composition of an outer layer of root hair?
Which part of the root helps in maximum absorption of water and minerals?
How many regions are there in a typical root?
Identify the part of the plants which is responsible for maximum absorption of water.
