Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the least possible distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
उत्तर
Let d be the least distance between the object and image for a real image formation.
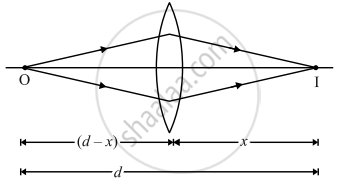
`1/f = 1/v - 1/u`, `1/f = 1/x + 1/(d - x) = d/(x(d - x))`
fd = xd - x2, x2 - dx + fd = 0, x = `(d ± sqrt(d^2 - 4fd))/2`
For real roots of x, d2 - 4fd ≥ 0
d ≥ 4f.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 12 cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is
- a convex lens of focal length 20 cm, and
- a concave lens of focal length 16 cm?
An object of size 3.0 cm is placed 14 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 21 cm. Describe the image produced by the lens. What happens if the object is moved further away from the lens?
The image of a small electric bulb fixed on the wall of a room is to be obtained on the opposite wall 3 m away by means of a large convex lens. What is the maximum possible focal length of the lens required for the purpose?
An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40 cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system, and the size of the image
An equiconvex lens of focal length 'f' is cut into two identical plane convex lenses. How will the power of each part be related to the focal length of the original lens ?
A convex lens forms a real image of a point object placed on its principals axis. If the upper half of the lens is painted black,
(a) the image will be shifted downward
(b) the image will be shifted upward
(c) the image will not be shifted
(d) the intensity of the image will decrease.
A pin of length 2.0 cm lies along the principal axis of a converging lens, the centre being at a distance of 11 cm from the lens. The focal length of the lens is 6 cm. Find the size of the image.
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light?
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
In the given figure the radius of curvature of the curved face in the planoconvex and the planoconcave lens is 15 cm each. The refractive index of the material of the lenses is 1.5. Find the final position of the image formed.