Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
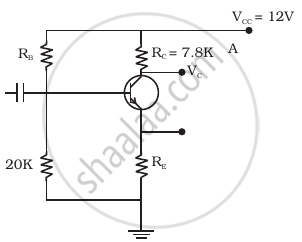
Show that the voltage gain, AV, of the amplifier is given by `A_v = (beta_(ac) R_1)/r_i`where βac is the current gain, RL is the load resistance and ri is the input resistance of the transistor. What is the significance of the negative sign in the expression for the voltage gain?
उत्तर
The expression for voltage gain of the transistor in CE configuration is:
`Av =V_0/V_2 = (-beta_(ac) R_L)/r`
βac → ac current gain
RL → Load resistance
r = RB + ri
ri → Input resistance
RB → Base resistance
Current gain of the transistor will decrease if the base is made thicker because current gain, `beta = I_c/I_b`
If the base of an n-p-n transistor is made thicker, then more and more electrons will recombine with the p-type material of the base. This results in a decrease in collector current Ic. Furthermore, Ib also increases.
Hence, ac current gain `(beta = I_c/I_b)`decreases.
Finding expression for voltage gain of the amplifier:
Applying Kirchhoff’ law to the output loop,
VCC = VCE + ICRC
VBB = VBE + IBRB
vi≠ 0
Then, VBB + vi = VBE + IBRB + ΔIB (RB + ri)
`because r_i = ((DeltaV_(BE))/(DeltaI_B))_(V_(CE))`
`therefore v_i = Delta I_B (R_B + r_i)`
`= rDelta I_B`
`beta_(ac) = (Delta I_c)/(DeltaI_B) = i_c/i_b`
It is current gain denoted by Ai.
Change IC due to change in IB causes a change in VCE and the voltage drop across resistor RC, because VCC is fixed.
` therefore DeltaV_("CC") = DeltaV_(CE)+R_cDeltaI_c=0`
`=> DeltaV_(CE)= -R_CDeltaI_C`
Change in VCE is the o/p voltage V0.
`therefore V_0 =DeltaV_(CE) = -beta_(ac)R_cDeltaI_B`
Voltage gain of amplifier
`A_v =V_0/V_i = (DeltaV_(CE))/(rDeltaI_B)`
`=-beta_(ac)=R_c/r`
Negative sign represents that the o/p voltage is in opposite phase to i/p voltage.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a simple circuit of a CE transistor amplifier. Explain its working ?
Let iE, iC and iB represent the emitter current, the collector current and the base current respectively in a transistor. Then
(a) iC is slightly smaller than iE
(b) iC is slightly greater than iE
(c) iB is much smaller than iE
(d) iB is much greater than iE.
In a normal operation of a transistor,
(a) the base−emitter junction is forward-baised
(b) the base−collector junction is forward-baised
(c) the base−emitter junction is reverse-baised
(d) the base−collector junction is reverse-baised.
Draw a circuit diagram of an n-p-n transistor with its emitter-base junction forward biased and basecollector junction reverse biased. Briefly describe its working.
Explain how a transistor in its active state exhibits a low resistance at its emitter-base junction and high resistance at its base-collector junction.
Derive the expression for the voltage gain of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration in terms of the load resistance RL, current gain a βa and input resistance.
Explain why input and output voltages are in opposite phase.
Draw a circuit diagram of an n-p-n transistor with its emitter-base junction forward biased and base-collector junction reverse biased. Briefly describe its working.
Explain how a transistor in its active state exhibits a low resistance at its emitter-base junction and high resistance at its base-collector junction.
Derive the expression for the voltage gain of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration in terms of the load resistance RL, current gain βa and input resistance.
Explain why input and output voltages are in the opposite phase.
Answer the following question.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying the output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Explain how the output characteristics is obtained.
For the transistor circuit shown in figure, evaluate VE, RB, RE given IC = 1 mA, VCE = 3 V, VBE = 0.5 V and VCC = 12 V, β = 100.