Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem.
A blacksmith fixes iron ring on the rim of the wooden wheel of a bullock cart. The diameter of the wooden rim and the iron ring are 1.5 m and 1.47 m respectively at room temperature of 27 °C. To what temperature the iron ring should be heated so that it can fit the rim of the wheel? (αiron = 1.2 × 10–5K–1).
उत्तर
Given: dw = 1.5 m, di = 1.47 m, T1 = 27 °C.
αi = 1.2 × 10–5/ K
To find: Temperature (T2)
Formula: α = `("d"_"w" - "d"_"i")/("d"_"i" ("T"_2 - "T"_1))`
Calculation: From formula,
`"T"_2 = ("d"_"w" - "d"_"i")/("d"_"i" alpha) + "T"_1`
`= (1.5 - 1.47)/(1.47 xx 1.2 xx 10^-5) + 27`
= 1700.7 + 27
= 1727.7 °C
Iron ring should be heated to temperature of 1727.7 °C.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A steel tape 1m long is correctly calibrated for a temperature of 27.0 °C. The length of a steel rod measured by this tape is found to be 63.0 cm on a hot day when the temperature is 45.0 °C. What is the actual length of the steel rod on that day? What is the length of the same steel rod on a day when the temperature is 27.0 °C? Coefficient of linear expansion of steel = 1.20 × 10–5 K–1
A brass rod of length 50 cm and diameter 3.0 mm is joined to a steel rod of the same length and diameter. What is the change in length of the combined rod at 250 °C, if the original lengths are at 40.0 °C? Is there a ‘thermal stress’ developed at the junction? The ends of the rod are free to expand (Co-efficient of linear expansion of brass = 2.0 × 10–5 K–1, steel = 1.2 × 10–5 K–1).
The coefficient of volume expansion of glycerin is 49 × 10–5 K–1. What is the fractional change in its density for a 30 °C rise in temperature?
If mercury and glass had equal coefficients of volume expansion, could we make a mercury thermometer in a glass tube?
If an automobile engine is overheated, it is cooled by pouring water on it. It is advised that the water should be poured slowly with the engine running. Explain the reason.
Is it possible for two bodies to be in thermal equilibrium if they are not in contact?
A gas thermometer measures the temperature from the variation of pressure of a sample of gas. If the pressure measured at the melting point of lead is 2.20 times the pressure measured at the triple point of water, find the melting point of lead.
The density of water at 0°C is 0.998 g cm–3 and at 4°C is 1.000 g cm–1. Calculate the average coefficient of volume expansion of water in the temperature range of 0 to 4°C.
A steel rod is clamped at its two ends and rests on a fixed horizontal base. The rod is unstrained at 20°C.
Find the longitudinal strain developed in the rod if the temperature rises to 50°C. Coefficient of linear expansion of steel = 1.2 × 10–5 °C–1.
A glass flask has a volume 1 × 10−4 m3. It is filled with a liquid at 30°C. If the temperature of the system is raised to 100°C, how much of the liquid will overflow? (Coefficient of volume expansion of glass is 1.2 × 10−5 (°C)−1 while that of the liquid is 75 × 10−5 (°C)−1).
A clock pendulum having coefficient of linear expansion. α = 9 × 10-7/°C-1 has a period of 0.5 s at 20°C. If the clock is used in a climate, where the temperature is 30°C, how much time does the clock lose in each oscillation? (g = constant)
A metal rod is heated to t°C. A metal rod has length, area of cross-section, Young's modulus and coefficient of linear expansion as 'L', 'A', 'Y' and 'a' respectively. When the rod is heated, the work performed is ______.
A metal rod of Young's moduls 'Y' and coefficient of linear expansion 'a' has its temeprature raised by 'Δ θ'. The linear stress to prevent the expansion of rod is ______.
(L and l is original length of rod and expansion respectively)
A metal rod of length Land cross-sectional area A is heated through T °C. What is the force required to prevent the expansion of the rod lengthwise?
(Y = Young's modulus of material of the rod, α = coefficient of linear expansion of the rod.)
The volume of a metal block changes by 0.86% when heated through 200 °C then its coefficient of cubical expansion is ______.
A uniform metallic rod rotates about its perpendicular bisector with constant angular speed. If it is heated uniformly to raise its temperature slightly ______.
An aluminium sphere is dipped into water. Which of the following is true?
As the temperature is increased, the time period of a pendulum ______.
A student records the initial length l, change in temperature ∆T and change in length ∆l of a rod as follows:
| S.No. | l(m) | ∆T (C) | ∆l (m) |
| 1. | 2 | 10 | `4 xx 10^-4` |
| 2. | 1 | 10 | `4 xx 10^-4` |
| 3. | 2 | 20 | `2 xx 10^-4` |
| 4. | 3 | 10 | `6 xx 10^-4` |
If the first observation is correct, what can you say about observations 2, 3 and 4.
Calculate the stress developed inside a tooth cavity filled with copper when hot tea at temperature of 57°C is drunk. You can take body (tooth) temperature to be 37°C and α = 1.7 × 10–5/°C, bulk modulus for copper = 140 × 109 N/m2.
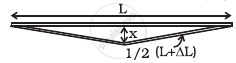
A rail track made of steel having length 10 m is clamped on a raillway line at its two ends (figure). On a summer day due to rise in temperature by 20° C, it is deformed as shown in figure. Find x (displacement of the centre) if αsteel = 1.2 × 10–5/°C.
The height of mercury column measured with brass scale at temperature T0 is H0. What height H' will the mercury column have at T = 0°C. Coefficient of volume expansion of mercury is γ. Coefficient of linear expansion of brass is α ______.
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
- Assertion A: When a rod lying freely is heated, no thermal stress is developed in it.
- Reason R: On heating, the length of the rod increases. In light of the above statements.
choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If the temperature of the sun were to increase from T to 2T and its radius from R to 2R, then the ratio of the radiant energy received on earth to what it was previously will be ______.
A glass flask is filled up to a mark with 50 cc of mercury at 18°C. If the flask and contents are heated to 38°C, how much mercury will be above the mark? (α for glass is 9 × 10-6/°C and coefficient of real expansion of mercury is 180 × 10-6/°C)
