Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Kirchhoff's rules and explain on what basis they are justified.
उत्तर
Kirchhoff’s first rule (Junction rule): The algebraic sum of the currents meeting at a point in an electrical circuit is always zero.
\[\sum_{} I = 0\]
This law is justified on the basis of law of conservation of charge.
Kirchhoff’s second law (Loop rule): In a closed loop, the algebraic sum of the emfs is equal to the algebraic sum of the products of the resistances and the current flowing through them.
\[\sum_{} I = 0\]
This law is justified on the basis of law of conservation of energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of 6 Ω?
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
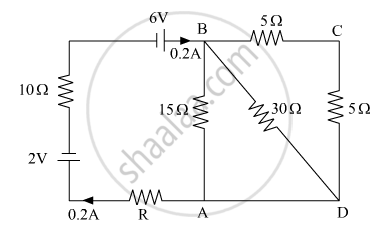
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points A and B?
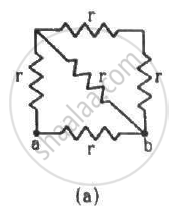
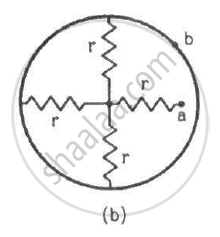
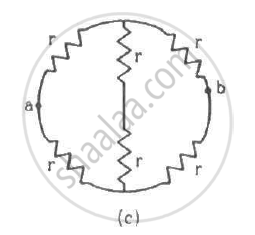
Find the equivalent resistances of the networks shown in the figure between the points a and b.
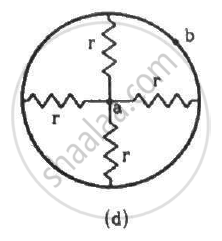
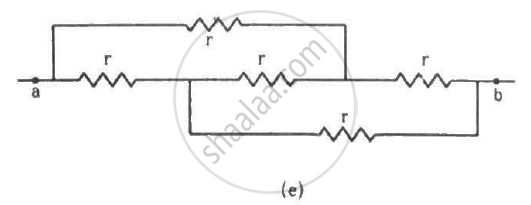
State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
Obtain the condition for bridge balance in Wheatstone’s bridge.
The e.m.f of The battery in a thermocouple is doubled. The rate of heat generated at one of the junction will.
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `i_3/i_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is: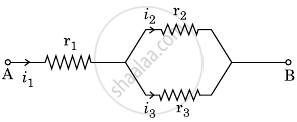
Derive the equation of the balanced state in a Wheatstone bridge using Kirchhoff’s laws.
