Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the reason to explain why covalent compounds "are bad conductors of electricity".
Give reason for the following:
Covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity.
उत्तर
In covalent compounds, electrons are stuck in the links between atoms instead of being able to move around freely. These molecules can't carry electricity without free ions or electrons that aren't stuck in one place.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give appropriate scientific reasons for Carbon tetrachloride does not conduct electricity.
Name the following:
The property of element by virtue of which atoms of the element can link to each other in the form of a long chain or ring structure.
How does graphite act as a lubricant?
What is buckminsterfullerene?
Explain why, ionic compounds conduct electricity in solution whereas covalent compounds do not conduct electricity.
Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of the element:
(a) phoshorus
(b) fluorine
(c) carbon
(d) sulphur
State the type of bonding in the following molecule.
Ammonium ion
Give two example in following case:
Solid covalent compounds
Draw an electron dot structure of the following molecule. (Without showing the circle) :
Water
Draw all possile structural formulae of compound from their molecular formula given below.
C4H10
The following structural formula belongs to which carbon compound?
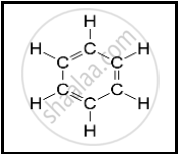
Give examples for the following:
Two gaseous polar compounds.
Explain the structure of Ammonium ion.
(a) Compound X consists of molecules.
Choose the letter corresponding to the correct answer from the choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below
The type of bonding in X will be
Element A has 2 electrons in its M shell. Element B has atomic number 7.
If B is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of A and B to form a compound.
Answer the following question.
What is methane? Draw its electron dot structure. Name the type of bonds formed in this compound. Why are such compounds:
(i) poor conductors of electricity? and
(ii) have low melting and boiling points? What happens when this compound burns in oxygen?
Explain covalent bond with example.
Discuss in brief about the properties of coordinate covalent compounds.
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H}\ce{H-C-H}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{C - H}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\]
