English Medium
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: मार्च 2014
Advertisements
Write any one difference in the electronic configurations of group-1 and group-2 elements ?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Write the contribution of Charles Darwin in the field of 'evolution.'
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Why do we need to manage our resources carefully?
Chapter: [0.14] Sources of Energy
List four modes of asexual reproduction.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
List two environment friendly practices or habits which need to be followed by every member of a family / community. Explain how these practices will support the "Save the environment" mission.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
"Affluent life style has a negative effect on the environment." Justify this statement with the help of an example.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
"Our food grains such as wheat and rice, the vegetables and fruits and even meat are found to contain varying amounts of pesticide residues." State the reason to explain how and why it happens?
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 ms−1, find the speed of light in a medium of absolute refractive index 1.5.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
What are esters ?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
How esters are prepared ?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
List two uses of esters.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Write the name and general formula of a chain of hydrocarbons in which an addition reaction with hydrogen is possible. State the essential condition for an addition reaction. Stating this condition, write a chemical equation giving the name of the reactant and the product of the reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Define the term : Valency
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Define the term : Atomic size
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
How do the valency and the atomic size of the elements vary while going from left to right along a period in the modern periodic table?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Consider two elements 'X' (Atomic number 17) and 'Y' (Atomic number 20)
(i) Write the positions of these elements in the modern periodic table giving justification.
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of 'X' and 'Y'.
(iii) Draw the electron-dot structure of the compound formed and state the nature of the bond formed between the two elements ?
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
On cutting the body of an organism into many pieces it was observed that many of these pieces developed as new individuals. Name the process and list two organisms in which this process may be observed. Draw a schematic diagram to illustrate the changes that are likely to be observed during the development of new individuals in any one of the organisms named.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List any four methods of contraception used by humans. State in brief two advantages of adopting such preventive methods.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Advertisements
"Birds have evolved from reptiles" State evidence to prove the statement.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Insects, octopus, planaria and vertebrates possess eyes. Can we group these animals together on the basis of eyes that they possess ? Justify your answer giving reason.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Mendel in one of his experiments with pea plants crossed a variety having round seed with one having wrinkled seeds. Write his observations, giving reasons, of F1 and F2 progeny
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events:
Twinkling of stars
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
About 45 lac people in the developing countries are suffering from corneal blindness. About 30 lac children below the age of 12 years suffering from this defect can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. How and why can students of your age involve themselves to create awareness about this fact among people?
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
State the reason why carbon can neither form \[\ce{C^4+}\] cations nor \[\ce{C^4−}\] anions but forms covalent compound.
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
State the reason to explain why covalent compounds "are bad conductors of electricity".
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
State the reason to explain why covalent compounds "have low melting and boiling points."
Chapter: [0.03] Metals and Non Metals [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give one example of a unisexual flower.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Advertisements
Write the site of fertilization and the part where the zygote gets implanted in the human female.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
You are asked by your teacher to study the different parts of an embryo of a gram seed. Given below are the steps to be followed for the experiment:
I. Soak the gram seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
II. Cut open a soaked seed and observe its different parts.
III. Take some dry gram seeds in a petri dish.
IV. Drain the excess water.
V. Cover the soaked seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is :
(A) III, I, V, IV, II
(B) III, I, II, IV, V
(C) III, IV, V, I, II
(D) III, I, IV, V, II
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Which one of the following pairs of vegetables is an example of homologous structures?
(A) Potato and sweet potato
(B) Carrot and radish
(C) Carrot and tomato
(D) Tomato and radish
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Four students P, Q, R and S differently reported the following set of organs to be analogous :
P. Forelimb of a frog and forelimb of a lizard
Q. Forelimb of a bird and forelimb of a human
R. Wings of a parrot and wings of a butterfly
S. Wings of a bird and wings of a bat
The two students who have reported correctly are :
(A) P and Q
(B) Q and R
(C) R and S
(D) P and S
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Identify the figures showing the process of budding in yeast.

(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) I, II and IV
(D) III, IV and I
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Study the following diagrams showing various stages of binary fission in Amoeba:
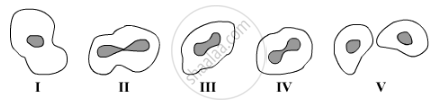
The correct sequence of these diagrams should be:
(A) I, IV, III, II, V
(B) I, III, IV, II, V
(C) I, II, IV, III, V
(D) I, II, III, IV, V
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A student adds a few drops of ethanoic acid to test tubes X, Y and Z containing aqueous solutions of sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate, respectively. If he now brings a burning splinter near the mouth of the test tubes immediately after adding ethanoic acid in each one of them, in which of the test tube or test tubes the flame will be extinguished?
(A) X and Y
(B) Y and Z
(C) X and Z
(D) only Z
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
When you add about 2 ml of acetic acid to a test tube containing an equal amount of distilled water and leave the test tube to settle after shaking its contents, what will you observe in the test tube after about 5 minutes?
(A) A white precipitate settling at its bottom
(B) A clear colourless solution
(C) A layer of water over the layer of acetic acid
(D) A layer of acetic acid over the layer of water
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
In order to study saponification reaction, we first prepare 20% solution of sodium hydroxide. If we record the temperature of this solution just after adding sodium hydroxide flakes to water and also test its nature using litmus, it may be concluded that the process of making this solution is
(A) exothermic and the solution is alkaline
(B) endothermic and the solution is alkaline
(C) endothermic and the solution is acidic
(D) exothermic and the solution is acidic
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
While studying saponification reaction for the preparation of soap, a teacher suggested to a student to add a small quantity of common salt to the reaction mixture. The function of common salt in this reaction is to
(A) reduce the alkalinity of the soap
(B) reduce the acidity of the soap
(C) enhance the cleansing capacity of soap
(D) favour precipitation of soap
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student takes about 6 ml of distilled water in each of the four test tubes P, Q, R and S. He then dissolves an equal amount of four different salts namely, sodium chloride in 'P', potassium chloride in 'Q', calcium chloride in 'R' and magnesium chloride in 'S'. Next, he then adds 10 drops of soap solution to each test tube and shakes its contents. The test tubes in which scum (insoluble substance) is formed with soap are:
(A) P and Q
(B) Q and R
(C) R and S
(D) Q and S
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed?
(A) Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(B) Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade
(C) Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade
(D) Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student has obtained an image of a distant object on a screen to determine the focal length F1 of the given lens. His teacher, after checking the image, gave him another lens of focal length F2 and asked him to focus the same object on the same screen. The student found that to obtain a sharp image, he has to move the lens away from the screen. From this finding, we may conclude that both the lenses given to the student were :
(A) Concave and F1 < F2
(B) Convex and F1 < F2
(C) Convex and F1 > F2
(D) Concave and F1 > F2
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student is observing a diagram showing the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism. He would find that for all angles of incidence the ray of light bends:
towards the normal, while entering the prism and away from the normal while emerging from the prism
away from the normal while entering the prism and towards the normal while emerging from the prism
away from the normal while entering as well as while emerging from the prism
towards the normal while entering as well as while emerging from the prism
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
The path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism is shown below:
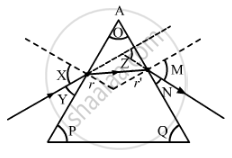
In this diagram, the angle of prism, angle of incidence, angle of emergence and angle of deviation, respectively, have been represented by:
(A) O, Y, Z and N,
(B) P, Y, M and Z,
(C) O, X, M and Z,
(D) P, X, Z and N.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
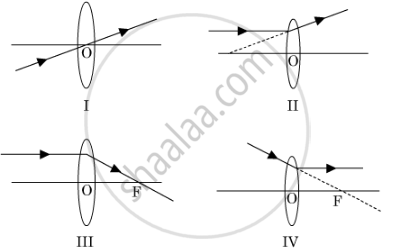
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student was asked by his teacher to find the image distance for various object distance in case of a given convex lens. He performed the experiment with all precautions and noted down his observations in the following table:
| S. No. |
Object distance (cm) |
Image distance (cm) |
| 1 | 60 | 15 |
| 2 | 48 | 16 |
| 3 | 36 | 21 |
| 4 | 24 | 24 |
| 5 | 18 | 36 |
| 6 | 16 | 48 |
After checking the observations table the teacher pointed out that there is a mistake in recording the image distance in one of the observations. Find the serial number of the observations having faulty image distance.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 5
(D) 6
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
On the basis of the experiment, "To trace the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab", students of a class arrived at which one of the following conclusions?
(A) Angle of incidence is greater than the angle of emergence.
(B) Angle of emergence is smaller than the angle of refraction.
(C) Emergent ray is parallel to the refracted ray.
(D) Incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Study the following four experimental set-ups I, II, III and IV for the experiment, "To trace the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab."
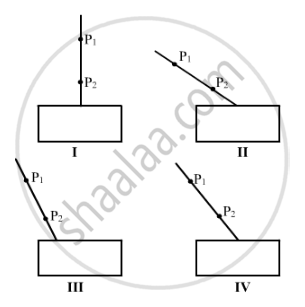
Which of the marked set-ups is likely to give best results (P1 and P2 are the positions of pins fixed on the incident ray)?
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
