Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two differences between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet.
उत्तर
| Electromagnet | Permanent magnet | |
| i. | It is made up of soft iron. | It is made up of steel. |
| ii. | The magnetic field strength can be changed. | The magnetic field strength cannot be changed. |
| iii. | Electromagnets of very strong field can be made. | Permanent magnets are not so strong. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is soft iron used as the core of the electromagnet in an electric bell?
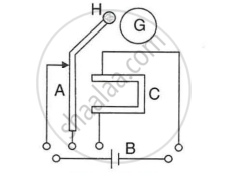
The incomplete diagram of an electric bell is given in Figure. Draw winding of coil on the core and complete the electric circuit in the diagram.
G-Gong, H-Hammer, A-Armature, C-Core, B-Battery.
Name one device that uses an electromagnet.
Electromagnets are made up of :
The strength of the electromagnet can be increased by
How is an electromagnet made? Name two factors on which the strength of magnetic field of the electromagnet depends.
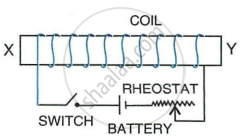
The following figure shows a coil wound around a soft iron bar XY.
- State the polarity at the ends X and Y as the switch is pressed.
- Suggest one way of increasing the strength of electromagnet so formed.
Show with the aid of a diagram how a wire is wound on a U-shaped piece of soft iron in order to make it an electromagnet. Complete the circuit diagram and label the poles of the electromagnet.
Name one device that uses an electromagnet.
State two advantages of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Why is soft iron used as the core of the electromagnet in an electric bell?
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
Explain, why steel is used in preference to soft iron for making permanent magnets while soft iron is used in preference to steel for making electromagnets.
Explain in detail the application of electromagnets.
Unlike magnetic poles ______ whereas like poles ______.
Assertion (A): When 2 long parallel wires, hanging freely are connected in parallel to a battery, they come closer to each other.
Reason (R): Wires carrying current in opposite directions repel each other.
Explain the working of the following device.
Speaker
