Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two differences between the e.m.f and terminal voltage of a cell.
उत्तर
| e.m.f. of cell | Terminal voltage of cell | |
| 1 | The amount of work required to move a unit positive charge in the entire circuit both inside and outside the cell serves as the measurement. | The amount of work required to move a unit of positive charge outside the cell serves as the measurement. |
| 2 | It is the characteristic of the cell i.e., it does not depend on the amount of current drawn from the cell | It depends on the amount of current drawn from the cell. The more current drawn from the cell, the lower the terminal voltage. |
| 3 | It is equal to the terminal voltage when the cell is not in use and greater than the terminal voltage when the cell is in use. | It is equal to the cell's EMf when it is not in use, while it is less than the EMf when it is in use. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the folloing blank with suitable words:
Current is measured in ............... using an ............... placed in ............... in a circuit.
Which type of circuit, series or parallel, is preferred while connecting a large number of bulbs:
(a) for decorating a hotel building from outside?
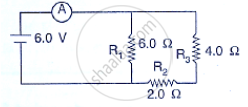
Three resistors of 6.0 𝛀, 2.0𝛀 and 4.0𝛀 are joined to an ammeter A and a cell of e.m.f. 6.0 V as
shown in fig 8.52 Calculate:
(a) the effective resistance of the circuit and
(b) the reading of ammeter.
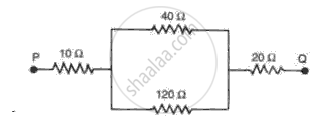
Find the effective resistance in the following circuit diagrams (Fig.):
Electrical appliances have voltage and power ratings as listed below. Which
has the larger working resistance?
| Appliances | Voltage (V) | Power (W) |
| (a) Washing machine | 250 | 3000 |
| ( b) Television | 240 | 160 |
| (c)240 | 240 | 1500 |
| ( d) Hair curler | 250 | 20 |
| ( e) Car head lamp | 12 | 36 |
Fill in the blank :
1 mA = ............................. A.
Match the following:
| 1. | 1 mA | a. | series |
| 2. | 1 pA | b. | ohmmeter |
| 3. | Ammeter | c. | 10-6 ampere |
| 4. | Electrical resistivity | d. | 10-3 ampere |
Problems for practice:
If 3A current flows through a circuit, then convert the current in terms of a milliampere.
