Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two factors upon which the rate of emission of thermions depends.
उत्तर
Factors on which the rate of emission of thermions depends:
1) Nature of the metal surface: Lower the work function of the metal, greater is the rate of emission of electrons.
2) The temperature of the surface: Higher the temperature of the surface, greater is the rate of emission of electrons.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the approximate value of specific latent heat of ice.
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
The S.I. unit of specific latent heat is ______.
Answer the following:
Explain the role of latent heat in the change of state of a substance.
Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
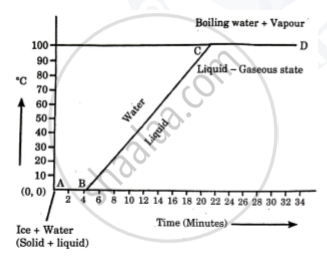
Define the following terms:
(i) Specific latent heat,
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion.
What is the name given to the energy absorbed during a phase change?
Why does weather become pleasant when it starts freezing in cold countries?
Why do we feel much comfortable when we sit under a moving fan especially when our body is sweating?
Derive an expression for the amount of heat given out or taken up, when its temperature falls or rises by t°C.
Calculate the total amount of heat required to convert 100g ice at 0°C to steam at 100°C.
(Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J/g, specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2260 J/g, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g°C).
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
If pressure increases, the melting point of a substance ______.
Define boiling point of a liquid.
Specific latent heat L = ______.
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 200g of ice at 0°C into the water at 0°C Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 Jg-1
The amount of heat energy required to melt a given mass of a substance at its melting point without any rise in its temperature is called as the ______.
