Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If pressure increases, the melting point of a substance ______.
विकल्प
does not change
decreases
increases
remains constant
उत्तर
If pressure increases, the melting point of a substance increases.
Explanation:
Most substances' melting points rise as pressure increases because the solid state is more compact than the liquid state. Higher pressure favors the solid phase, necessitating additional heat (higher temperature) to overcome this and cause melting. Ice is an exception to this rule, as its melting point decreases under pressure due to its unusual structure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which has more heat: 1 g ice at 0℃ or 1g water 0℃? Give reason.
A refrigerator converts 100g of water at 20℃ to ice at – 10℃ in 73.5 min. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in watt. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J kg-1 K-1, specific latent heat of ice is 336 J g-1 and the specific heat capacity of ice is 2.1 J kg-1 K-1.
Answer the following:
Explain the role of latent heat in the change of state of a substance.
Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
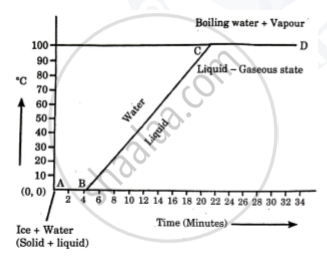
Derive an expression for the amount of heat given out or taken up, when its temperature falls or rises by t°C.
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
If there is no Heat loss to the surroundings, the heat released by the condensation of m1 g of steam at 100°C into water at 100°C can be used to convert m2 g of ice at 0°C into water at 0°C.
(i) Find:
(a) The heat lost by steam in terms of m1
(b) The heat gained by ice in terms of m2
(ii) Form a heat equation find the ratio of m2 : m1
Specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2268 kJ/kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 kJ/kg
Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C
How fog is formed?
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Specific latent heat of fusion | a) Air saturated with vapour |
| 2) Specific latent heat of vaporisation | b) Solid converts into liquid |
| 3) Dew point temperature | c) liquid converts into gas |
1 kg of dry air at a temperature of 40 °C can hold a maximum of 49 g of water vapour.
Write scientific reason.
The bottom of some steel utensils used for cooking is copper.
Define specific latent heat capacity
For the same mass of ice and ice-cold water, why does ice produce more cooling than ice-cold water?
600 g of copper at 50°C is mixed with lOOOg water at 20°C. Find the final temperature of the mixture. The specific heat capacity of copper is 0.4 Jg-1°C-1 and that of water is 4.2 Jg-1°C-1
2875 J of heat is required to melt 115 g of lead at its melting point. Calculate the specific latent heat capacity of fusion of lead.
Observe the following graph and answer the following questions:

- What does the graph represent?
- What does the line AB represent?
- What does the line BC represent?
20 g of ice at 0°C absorbs 10,920 J of heat energy to melt and change to water at 50°C. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. Specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg-1 K-1.
