Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which has more heat: 1 g ice at 0℃ or 1g water 0℃? Give reason.
Which will contain more heat energy 1 g of ice at 0°C or 1 g water at 0°C?
उत्तर १
1 g of water at 0°C has more heat than 1 g of ice at 0°C. This is because ice at 0°C absorbs 360 J of heat energy to convert into water at 0°C.
उत्तर २
At 0°C, 336 J of heat energy is taken in by ice, turning it into water. Water therefore has higher heat energy at 0°C.
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the effect of an increase of impurities on the melting point of ice.
Write the approximate value of specific latent heat of ice.
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
Explain the following:
The heat supplied to a substance during it change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature.
The specific latent heat of fusion of water is ______.
What is meant by latent heat? How will the state of matter transform if latent heat is given off?
When a liquid is getting converted into solid, the latent heat is ………………………………
Water expands on reducing its temperature below ______°C.
What do you mean by the statement?
'The specific latent heat capacity of fusion of ice is 336 J per g'?
Explain the statement; “The specific latent heat of vaporization of wafer is 2260 × 103 J/kg”.
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
During reheating, ice is converted to water at a temperature of 0 °C.
Write scientific reason.
Even if boiling water is constantly heated, its temperature does not rise.
For the same mass of ice and ice-cold water, why does ice produce more cooling than ice-cold water?
Who introduced the term latent heat?
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 200g of ice at 0°C into the water at 0°C Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 Jg-1
The amount of heat energy required to melt a given mass of a substance at its melting point without any rise in its temperature is called as the ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for a substance:
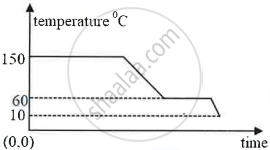
- State the temperatures at which the substance condenses.
- The temperature range in which the substance is in liquid state.
- Why do we prefer ice to ice-cold water for cooling a drink?
