Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Students should take examples of their own and practise the construction of triangles.
उत्तर
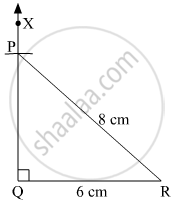
In ∆PQR, l(PR) = 8 cm, m ∠PQR = 90° , l(QR) = 6 cm.
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line QR = 6 cm.
- With Q as centre, draw ∠XQR = 90º.
- With R as centre and 8 cm as radius, cut an arc on XQ and name it as point P.
- Join PR.
∆PQR is thus formed.
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ∆ STU, l(ST) = 7 cm, l(TU) = 4 cm, l(SU) = 5 cm
Draw triangle with the measures given below.
In ∆ NTS, m ∠T = 40°, l(NT) = l(TS) = 5 cm
Construct a triangle of the measures given below.
In ∆LMN, l(LM) = 6.2 cm, m∠LMN = 60°, l(MN) = 4 cm. Construct ∆LMN.
Construct a triangle using the given data: BC = 6.0cm, ∠B = 60° and ∠C = 45°
Construct an isosceles triangle in which: XY = XZ, YZ = 5.5 cm and ∠X = 60°
Construct an equilateral triangle using the given data: Altitude OM = 5.8 cm
Construct a triangle using the given data: AB - AC = 1.2 cm, BC = 6.0 cm and ∠B = 60°
Construct a triangle using the given data: Perimeter of triangle is 6.4 cm, and the base angles are 60° and 45°
Construct a ΔPQR with ∠Q = 60°, ∠R = 45° and the perpendicular from P to QR be 3.5 cm. Measure PQ.
