Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Students should take examples of their own and practise the construction of triangles.
उत्तर
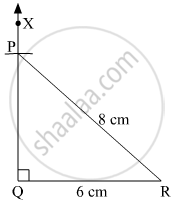
In ∆PQR, l(PR) = 8 cm, m ∠PQR = 90° , l(QR) = 6 cm.
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line QR = 6 cm.
- With Q as centre, draw ∠XQR = 90º.
- With R as centre and 8 cm as radius, cut an arc on XQ and name it as point P.
- Join PR.
∆PQR is thus formed.
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ∆ STU, l(ST) = 7 cm, l(TU) = 4 cm, l(SU) = 5 cm
Draw triangle with the measures given below.
In ∆FUN, l(FU) = 5 cm, l(UN) = 4.6 cm, m∠U = 110°
Construct a triangle of the measures given below.
In ∆MNP, l(NP) = 5.2 cm, m∠N = 70°, m ∠P = 40°
Construct a triangle of the measures given below.
Construct a triangle of the measures given below.
In ∆ABC, l(AC) = 7.5 cm, m ∠ABC = 90°, l(BC) = 5.5 cm.
Construct a triangle using the given data: DE = 6.5cm, EF = 5.8cm and DF = 4.2cm
Construct a triangle using the given data: PQ = 6.2cm, QR = 9.0cm and ∠Q = 30°
Construct a right-angled triangle in which: Side AB = 4.5 cm and hypotenuse AC = 7 cm
Construct an equilateral triangle using the given data: Altitude PM = 3.6 cm
Construct a ΔXYZ with YZ = 7.5 cm, ∠Y = 60° and ∠Z = 45°. Draw the bisectors of ∠Y and ∠Z. If these bisectors meet at O, measure angle YOZ.
