Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose a ‘n’-type wafer is created by doping Si crystal having 5 × 1028 atoms/m3 with 1 ppm concentration of As. On the surface 200 ppm Boron is added to create ‘P’ region in this wafer. Considering n i = 1.5 × 1016 m–3, (i) Calculate the densities of the charge carriers in the n and p regions. (ii) Comment which charge carriers would contribute largely for the reverse saturation current when diode is reverse biased.
उत्तर
(i) n-type wafer is created when As is implanted in Si crystal. The number of majority carriers electrons due to doping of As is
`n_e = N_D`
= `10^-6 xx 5 xx 10^28` atoms/m3
= `5 xx 10^22/m^3`
The number of minority carriers (holes) in an n-type wafer is
`n_h = n_i^2/n_e`
= `(1.5 xx 10^16)^2/(5 xx 10^22)`
= `0.45 xx 10^10/m^3`
The p-type wafer is created with the number of holes, when Boron is implanted in Si crystal,
`n_h = N_A`
= `200 xx 10^-6 xx (5 xx 10^28)`
= `1 xx 10^25/m^3`
Minority carriers (electrons) created in the p-type wafer is
`n_e = n_i^2/n_h`
= `(1.5 xx 10^16)^2/(1 xx 10^25)`
= `2.25 xx 10^7/m^3`
(ii) The minority carrier holes of the n-region wafer (nh = 0.45 × 1010/m3) would contribute more to the reverse saturation current than minority carrier electrons (ne = 2.25 × 107/m3) of the p-region wafer when the p-n junction is reverse biased.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between 'intrinsic' and 'extrinsic' semiconductors
In a p-type semiconductor, the acceptor impurity produces an energy level ______
A donor impurity results in ______.
In p-type semiconductor, ______.
Distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors.
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because ______.
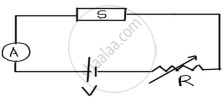
The figure shows a piece of pure semiconductor S in series with a variable resistor R and a source of constant voltage V. Should the value of R be increased or decreased to keep the reading of the ammeter constant, when semiconductor S is heated? Justify your answer
Two crystals C1 and C2, made of pure silicon, are doped with arsenic and aluminium respectively.
Identify the extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
- Assertion (A): Putting the p-type semiconductor slab directly in physical contact with the n-type semiconductor slab cannot form the pn junction.
- Reason (R): The roughness at contact will be much more than inter atomic crystal spacing and continuous flow of charge carriers is not possible.
The majority charge carriers in a P-type semiconductor are ______.
