Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Supposing Newton’s law of gravitation for gravitation forces F1 and F2 between two masses m1 and m2 at positions r1 and r2 read F1 = – F2 = `- r_12/r_12^3 GM_0^2 ((m_1m_2)/M_0^2)^n` where M0 is a constant of dimension of mass r12 = r1 – r2 and n is a number. in such a case.
- the acceleration due to gravity on earth will be different for different objects.
- none of the three laws of Kepler will be valid.
- only the third law will become invalid.
- for n negative, an object lighter than water will sink in water.
उत्तर
a, c and d
Explanation:
Given, `F_1 = - F_2 = (-r_12)/r_12^3 GM_0^2 ((m_1m_2)/m_0^2)^n`
Acceleration due to gravity, `g = (|F|)/"mass"`
= `(GM_0^2 (m_1m_2)^n)/(r_12^2 (M_0)^(2n)) xx 1/(("mass"))`
Since. g depends upon the position vector, hence it will be different for different objects. As g is not constant, hence constant of proportionality will not be constant in Kepler's third law. Hence, Kepler's third law will not be valid.
As the force is of central nature. .....`[∵ "Force" ∝ 1/r^2]`
Hence, the first two of Kepler's laws will be valid.
For negative n, g = `(GM_0^2 (m_1m_2)^-n)/(r_12^2 (M_0)^(-2n)) xx 1/(("mass"))`
= `(GM_0^(2(1 + n)))/r_12^2 ((m_1m_2)^-n)/(("mass"))`
g = `(GM_0^2)/r_12^2 (M_0^2/(m_1m_2)) xx 1/"mass"`
As M0 > m1 or m2
g > 0, hence in this case situation will reverse i.e., an object lighter than water will sink in water.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A comet orbits the Sun in a highly elliptical orbit. Does the comet have a constant (a) linear speed, (b) angular speed, (c) angular momentum, (d) kinetic energy, (e) potential energy, (f) total energy throughout its orbit? Neglect any mass loss of the comet when it comes very close to the Sun.
A Saturn year is 29.5 times the earth year. How far is the Saturn from the sun if the earth is 1.50 ×108 km away from the sun?
In the Following figure shows the elliptical path of a planet about the sun. The two shaded parts have equal area. If t1 and t2 be the time taken by the planet to go from a to b and from c to d respectively,
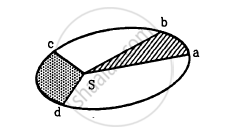
Answer the following question.
State Kepler’s law of equal areas.
The square of its period of revolution around the sun is directly proportional to the _______ of the mean distance of a planet from the sun.
Write the Kepler's laws.
The third law of Kepler is also known as the Law of ______.
Give one example each of central force and non-central force.
Out of aphelion and perihelion, where is the speed of the earth more and why?
Earth’s orbit is an ellipse with eccentricity 0.0167. Thus, earth’s distance from the sun and speed as it moves around the sun varies from day to day. This means that the length of the solar day is not constant through the year. Assume that earth’s spin axis is normal to its orbital plane and find out the length of the shortest and the longest day. A day should be taken from noon to noon. Does this explain variation of length of the day during the year?
