Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The choice of a reducing agent in a particular case depends on thermodynamic factor. How far do you agree with this statement? Support your opinion with two examples.
उत्तर १
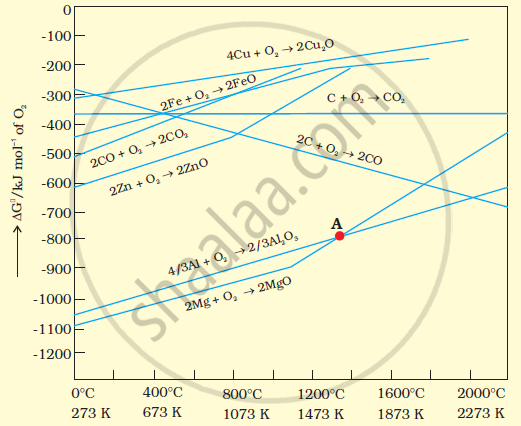
The above figure is a plot of Gibbs energy (`triangleG^theta`)vs. T for formation of some oxides.
It can be observed from the above graph that a metal can reduce the oxide of other metals, if the standard free energy of formation (`triangle_fG^theta`) of the oxide of the former is more negative than the latter. For example, since `triangle_fG_(Al,Al_2,O_3)^theta` is more negative than `triangle_fG_(Cu,Cu_2.O)^theta`, Al can reduce Cu2O to Cu, but Cu cannot reduce Al2O3. Similarly, Mg can reduce ZnO to Zn, but Zn cannot reduce MgO because `triangle_fG_(" " (Mg,MgO))^theta` is more negative than `triangle_fG_("" (Zn,ZnO))^(theta)`.
उत्तर २
We can study the choice of a reducing agent in a particular case using Ellingham diagram.
It is evident from the diagram that metals for which the standard free energy of formation oftheir oxides is more negative can reduce those metal oxides for which the standard free energy of formation of their respective oxides is less negative. It means that any metal will reduce the oxides of other metals which lie above it in the Ellingham diagram. This is because the standard free energy change (ΔrG°) of the combined redox reaction will be negative by an amount equal to the difference in Δf G° of the two metal oxides. Thus both Al and Zn can reduce FeO to Fe but Fe cannot reduce Al203 to A1 and ZnO to Zn. In the same way, G can reduce ZnO to Zn but not CO.
Note : Only that reagent will be preferred as reducing agent which will lead to decrease in free energy value (ΔG°) at a certain specific temperature
उत्तर ३
We can study the choice of a reducing agent in a particular case using Ellingham diagram.
It is evident from the diagram that metals for which the standard free energy of formation oftheir oxides is more negative can reduce those metal oxides for which the standard free energy of formation of their respective oxides is less negative. It means that any metal will reduce the oxides of other metals which lie above it in the Ellingham diagram. This is because the standard free energy change (ΔrG°) of the combined redox reaction will be negative by an amount equal to the difference in Δf G° of the two metal oxides. Thus both Al and Zn can reduce FeO to Fe but Fe cannot reduce Al203 to A1 and ZnO to Zn. In the same way, G can reduce ZnO to Zn but not CO.
Note : Only that reagent will be preferred as reducing agent which will lead to decrease in free energy value (ΔG°) at a certain specific temperature
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is the extraction of copper from pyrites more difficult than that from its oxide ore through reduction?
Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron.
State the role of silica in the metallurgy of copper.
Write chemical reactions taking place in the extraction of copper from Cu2 S.
How will you convert the following:
Zinc blende to Zinc metal
The impurity that is added externally to remove the impurity already present in the ore is known as ____________.
Choose the correct option of temperature at which carbon reduces \[\ce{FeO}\] to iron and produces \[\ce{CO}\].
For the reduction of \[\ce{FeO}\] at the temperature corresponding to point D, which of the following statements is correct?
For the metallurgical process of which of the ores calcined ore can be reduced by carbon?
(i) Haematite
(ii) Calamine
(iii) Iron pyrites
(iv) Sphalerite
Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron?
The mixture of compounds A and B is passed through a column of \[\ce{Al2O3}\] by using alcohol as eluant. Compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Which of the compounds A or B, is more readily adsorbed on the column?
Why is sulphide ore of copper heated in a furnace after mixing with silica?
Write down the reactions taking place in Blast furnace related to the metallurgy of iron in the temperature range 500-800 K.
Explain the following:
Generally sulphide ores are converted into oxides before reduction.
Carbon deposition reaction taking place in ______.
