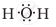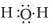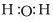Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is
विकल्प
उत्तर

Explanation -
The central atom in water molecule is oxygen. It has 6 electrons in its valence shell and shares one electron each from the two hydrogen atoms.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a chemical test to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Why are certain compounds called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction that converts alkenes into alkanes and also write a chemical equation to show the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur.
Write the electron-dot structures for ethyne.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Ethyne has ......... carbon-hydrogen single bonds.
You are given the following molecular formulae of some hydrocarbons:
C5H8; C7H14; C6H6; C5H10; C7H12; C6H12
Which two formulae represent unsaturated hydrocarbons having triple bonds?
What happens when vegetable oils are hydrogenated? Name the catalyst used.
Which of the following hydrocarbons can decolourise bromine water and which cannot? Why?
C6H12, C6H14, C6H10
The name of the compound CH3 — CH2 — CHO is
The formulae of four organic compounds are shown below. Choose the correct option
| A | B | C | D |
| \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{H}\\ \phantom{.}\backslash\phantom{.....}/\\ \ce{C = C}\\ /\phantom{.....}\backslash\\ \ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{H} \end{array}\] |
\[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{........}\ce{H}\phantom{.....}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.......}|\phantom{....}//\\ \ce{H - C - C}\\ \phantom{......}|\phantom{.....}\backslash\\ \phantom{...........}\ce{H}\phantom{.....}\ce{O - H} \end{array}\] |
\[\begin{array}{cc}
|
\[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}\\ \ce{H - C - C - O - H}\\ |\phantom{....}|\phantom{.....}\\ \ce{H}\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{.....} \end{array}\] |