Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
(i) Saturated Hydrocarbons: The compounds of carbon having only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called saturated compounds. This includes alkanes, having a general formula CnH2n+2.
(ii) Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: The compounds of carbon having double and triple bonds between the carbon atoms are called unsaturated compounds. This includes alkenes and alkynes having general formula CnH2n and CnH2n-2, respectively.
Example
(i) Saturated hydrocarbon: C2H6 (Ethane)
Structure:
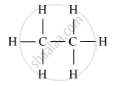
Structure:
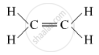
Structure:
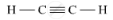
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define Saturated hydrocarbon.
What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Draw the electron dot structures for ethanoic acid.
Draw the electron dot structures for propanone.
Why are certain compounds called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction that converts alkenes into alkanes and also write a chemical equation to show the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur.
A compound 'X' on heating with excess conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K gives an unsaturated compound 'Y'. 'X' also reacts with sodium metal to evolve a colourless gas 'Z'. Identify 'X', 'Y' and 'Z'. Write the equation of the chemical reaction of formation of 'Y' and also write the role of sulphuric acid in the reaction.
What happens when vegetable oils are hydrogenated? Name the catalyst used.
Fill in the blanks and rewrite the completed statements:
The organic compounds having double or triple bond in them are termed as _________________ _________________.
Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.........}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..........}\\
\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......}/\phantom{................}|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{............}\\
\ce{C} = \ce{C} + \ce{H2} \overset{\ce{Ni}}{\rightarrow} \ce{CH3 - C - C - CH3}\\
\phantom{.}/\phantom{........}\backslash\phantom{..............}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{............}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{........}
\end{array}\] - \[\ce{CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH \overset{\ce{Conc. H2SO4}}{\rightarrow}CH3COOC2H5 + H2O}\]
- \[\ce{CH3CH2OH}\ce{->[Alk.KMnO4][Heat]CH3COOH}\]
