Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
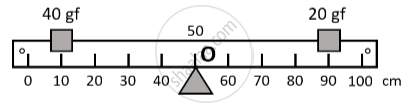
The figure shows a uniform metre rule placed on a fulcrum at its mid-point O and having a weight 40 gf at the 10 cm mark and a weight of 20 gf at the 90 cm mark.
- Is the metre rule in equilibrium? If not how will the rule turn?
- How can the rule be brought in equilibrium by using an additional weight of 40 gf?
उत्तर
W1 × d1 = W2 × d2
40 × 40 = 20 × 40
1600 ≠ 800
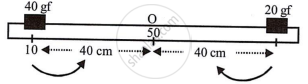
Anticlockwise moment ≠ clockwise moment
- No, the rule will turn anticlockwise
Anticlockwise moment > clockwise moment. - Moment of force needed = 800
Where 40 gf additional should be placed
1600 = 800 + 40 × d
∴ 40d = 1600 − 800 = 800
d = `800/40 = 20` cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two condition for a body acted upon by several forces to be in equilibrium.
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
What do you mean by the state of equilibrium? What are the conditions for stable equilibrium?
Give scientific reason for the following:
While climbing a hill you will try to bend your body forward.
In figure, a uniform bar of length l m is supported at its ends and loaded by a weight W kgf at its middle. In equilibrium, find the reactions R1 and R2 at the ends.
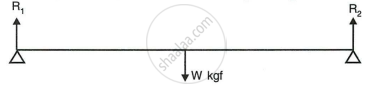
`["Hint:" "In equilibrium" "R"_1 + "R"_2 = "W" "and" "R"_1 xx l/2 = "R"_2 xx l/2]`
One end of a spring is kept fixed while the other end is stretched by a force as shown in the diagram.
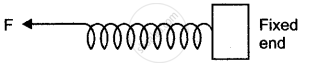
(i) Copy the diagram and mark on it the direction of the restoring force.
(ii) Name one instrument which works on the above principle.
Give an experiment to verify the principle of moments.
What are the three types of stability of an object?
