Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
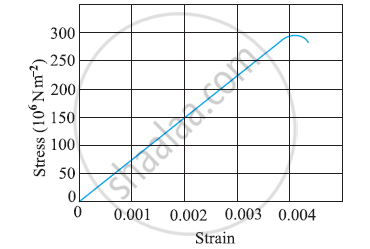
The figure shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young’s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?
उत्तर
a) Young’s modulus of the material (Y) is given by
Y =Stress/Strain
=150 x 106/0.002
150 x 106/2 x 10-3
=75 x 109 Nm-2
=75 x 1010 Nm-2
b) Yield strength of a material is defined as the maximum stress it can sustain. From graph, the approximate yield strength of the given material
= 300 x 106 Nm-2
= 3 x 108 Nm-2 .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are shown in Figure
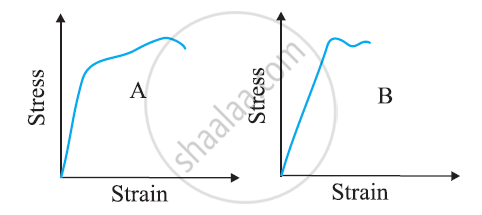
The graphs are drawn to the same scale.
(a) Which of the materials has the greater Young’s modulus?
(b) Which of the two is the stronger material?
Two wires A and B are made of same material. The wire A has a length l and diameter rwhile the wire B has a length 2l and diameter r/2. If the two wires are stretched by the same force, the elongation in A divided by the elongation in B is
A steel rod of cross-sectional area 4 cm2 and 2 m shrinks by 0.1 cm as the temperature decreases in night. If the rod is clamped at both ends during the day hours, find the tension developed in it during night hours. Young modulus of steel = 1.9 × 1011 N m−2.
A copper wire of cross-sectional area 0.01 cm2 is under a tension of 20N. Find the decrease in the cross-sectional area. Young modulus of copper = 1.1 × 1011 N m−2 and Poisson ratio = 0.32.
`["Hint" : (Delta"A")/"A"=2(Delta"r")/"r"]`
Young's modulus of a perfectly rigid body is ______.
The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s modulus of elasticity ______.
What is the Young’s modulus for a perfect rigid body ?
A truck is pulling a car out of a ditch by means of a steel cable that is 9.1 m long and has a radius of 5 mm. When the car just begins to move, the tension in the cable is 800 N. How much has the cable stretched? (Young’s modulus for steel is 2 × 1011 Nm–2.)
In nature, the failure of structural members usually result from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by `(Ypir^4)/(4R) . Y` is the Young’s modulus, r is the radius of the trunk and R is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along the height of the tree containing the centre of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
If the length of a wire is made double and the radius is halved of its respective values. Then, Young's modules of the material of the wire will ______.
