Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following sketch illustrates the process of conversion of Alumina to Aluminium:
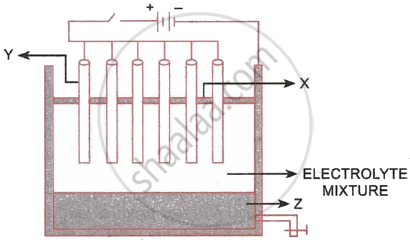
- Name the constituent of the electrolyte mixture which has a divalent metal in it.
- Name the powdered substances ‘X’ sprinkled on the surface of the electrolyte mixture.
- What is the name of the process?
- Write the reactions taking place at the electrodes ‘Y’ (anode) and ‘Z’ (cathode), respectively.
उत्तर
- The electrolytes used are molten alumina, cryolite and fluospar.
- Powdered coke layer (X).
- Hall Heroult process
- Cathode (Z): \[\ce{Al^{3+} + 3e^{-} -> Al}\]
Anode (Y): \[\ce{C + 2O^{2+} -> CO_2 + 4e^{-}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the solution used to react with Bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminum oxide, in the Baeyer’s process
Name the constituents of Duralumin.
Name the constituents of Solder.
In order to obtain 1 tonne of aluminium, the following inputs are required: 4 tonnes of bauxite, 150 kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 kg of graphite. The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (III) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
- Name the process used for the purification of bauxite.
- Write the equation for the action of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
Aluminium is a more active metal than iron, but suffers less corrosion. Why?
Explain and give reasons why aluminium vessels should not be cleaned with powders containing alkalis.
For the substance listed below, explain its role in the extraction of aluminium: Bauxite
Name the compound added to pure alumina to lower the fusion temperature during the electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Name the alloy used for the following purpose.
Surgical instruments
In Hall and Heroult's process, products liberated at anode and cathode are ______
