Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The following sketch illustrates the process of conversion of Alumina to Aluminium:
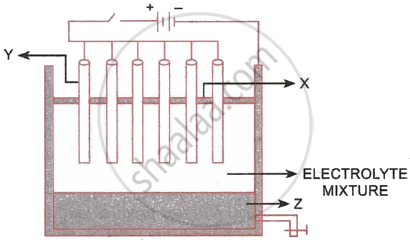
- Name the constituent of the electrolyte mixture which has a divalent metal in it.
- Name the powdered substances ‘X’ sprinkled on the surface of the electrolyte mixture.
- What is the name of the process?
- Write the reactions taking place at the electrodes ‘Y’ (anode) and ‘Z’ (cathode), respectively.
Solution
- The electrolytes used are molten alumina, cryolite and fluospar.
- Powdered coke layer (X).
- Hall Heroult process
- Cathode (Z): \[\ce{Al^{3+} + 3e^{-} -> Al}\]
Anode (Y): \[\ce{C + 2O^{2+} -> CO_2 + 4e^{-}}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the solution used to react with Bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminum oxide, in the Baeyer’s process
Write the equation for the reaction where the aluminum oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminum is obtained by heating aluminum hydroxide.
Explain with reason:
Carbon can reduce lead oxide but not aluminium oxide.
Name the constituents of Brass.
Name the following:
The materials used as electrodes in the electrolytic extraction of aluminium.
For the substance listed below, explain its role in the extraction of aluminium: Sodium hydroxide
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Name a chemicals used for dissolving aluminium oxide. In which state of sub-division is the chemical used?
Write the constituents of the electrolyte for the extraction of aluminium.
Write the balanced chemical equation to show the concentration of ore in Baeyer’s process.
Aluminium hydroxide to alumina
What impurities are present in aluminium ore?
