Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The minimum frequency for photoelectric effect on metal is 7 × 1014 Hz, Find the work function of the metal.
उत्तर
Work function, `phi_0` = hν0
= 6.63 × 10−34 × 7 × 1014
= 4.641 × 10−19 J
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive material is doubled, then the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron will be ______.
What is the photoelectric effect?
Find the energy of photon which have momentum 2 × 10-16 gm-cm/sec.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
The maximum velocity of photoelectron emitted is 4.8 m/s. If the e/m ratio of the electron is 1.76 × 1011 C/kg, then stopping potential is given by ______
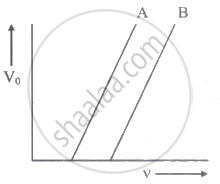
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
When light falls on a metal surface, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons depends upon ______
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in photoelectric effect is 3.2 × 10-19 J and the work-function for metal is 6.63 × 10-19 J, then stopping potential and threshold wavelength respectively are
[Planck's constant, h = 6.63 × 1034 J-s]
[Velocity of light, c = 3 × 108 `"m"/"s"`]
[Charge on electron= 1.6 × 10-19 C]
Threshold frequency for a metal is 1015 Hz. Light of `lambda` = 4000 Å falls on its surface. Which of the following statements is correct?
A metal surface is illuminated by light of given intensity and frequency to cause photoemission. If the intensity of illumination is reduced to one-fourth of its original value then the maximum KE of the emitted photoelectrons would be ______.
The work function of a metallic surface is 5.01 eV. The photoelectrons are emitted when light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on it. The potential difference applied to stop the fastest photoelectrons is [h = 4.14 x 10-15 eV sec] ____________.
In photoelectric experiment, if both the intensity and frequency of the incident light are doubled, then the saturation of photoelectric current ______.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
When a surface 1 cm thick is illuminated by light of wavelength 'λ', the stopping potential is 'V0'. When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength '3λ', the stopping potential is `"V"_0/6`. The threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is ______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
A light of wavelength '`lambda`' and intensity 'I' falls on photosensitive material. If 'N' photoelectrons are emitted, each with kinetic energy E, then ____________.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
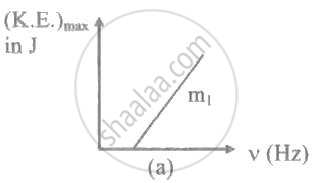
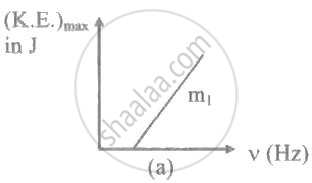
The ratio of slopes m1: ro2 of the lines given in the following graphs is, ______.
Which one of the following graphs represents the variation of photoelectric current (i) with intensity (I) of the incident light?
For a given photosensitive material and frequency (> threshold frequency) of incident radiation, the photoelectric current varies with the intensity of incident light as:
On a photosensitive material when frequency of incident radiation is increased by 30%, kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons increases from 0.4 eV. The work function of the surface is ______.
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Explain the failure of wave theory of light to account for the observations from experiments on photoelectric effect.
Define photoelectric work function of a metal.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
