Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, if in photoelectric effect energy of incident Photon is 4 eV and work function is 2.4 eV.
उत्तर
K.E.max = hν − φ0
= 4 − 2.4
= 1.6 eV.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive material is doubled, then the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron will be ______.
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
The minimum frequency for photoelectric effect on metal is 7 × 1014 Hz, Find the work function of the metal.
The work function of a surface is 3.1 eV. A photon of frequency 1 × 1015 Hz. Is an incident on it. Calculate the incident wavelength is photoelectric emission occurs or not.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is v. Charge and the mass of the photoelectron is denoted by e and m, respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
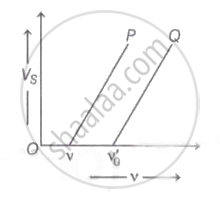
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in photoelectric effect is 3.2 × 10-19 J and the work-function for metal is 6.63 × 10-19 J, then stopping potential and threshold wavelength respectively are
[Planck's constant, h = 6.63 × 1034 J-s]
[Velocity of light, c = 3 × 108 `"m"/"s"`]
[Charge on electron= 1.6 × 10-19 C]
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
When certain metal surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength A., the stopping potential is V, When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is `("V"/3)`. The threshold wavelength for the surface is ______.
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
Which one of the following statements ts INCORRECT for stopping potential in photoelectric emission?
A light of wavelength '`lambda`' and intensity 'I' falls on photosensitive material. If 'N' photoelectrons are emitted, each with kinetic energy E, then ____________.
When a metal with work function 0.6 eV is illuminated with light of energy 2 eV, the stopping potential will be ____________.
The ratio of slopes m1: ro2 of the lines given in the following graphs is, ______.
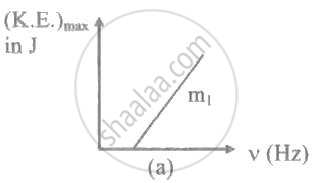
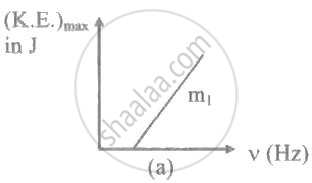
A light of frequency 'v' is incident on the metal surface whose threshold frequency is 'v0'. If v = v0, then [c = speed of light in medium] ____________.
The radiation emitted, when an electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 orbit is a hydrogen atom, falls on a metal to produce photoelectron. The electrons from the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy are made to move perpendicular to a magnetic field of `1/320`T in a radius of 10-3m. Find the 320 work function of metal:
We wish to observe an object which is 2.5Å in size. The minimum energy photon that can be used ______.
A charged dust particle of radius 5 × 10-7 m is located in a horizontal electric field having an intensity of 6.28 × 105 V/m. The surrounding medium is air with a coefficient of viscosity η = 1.6 × 10-5 N-s/m2. If the particle moves with a uniform horizontal speed of 0.02 m/s, the number of electrons on it is ______.
Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitive metallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons is ______.
In a photocell, frequency of incident radiation is increased by keeping other factors constant (v > v0), the stopping potential ______.
On a photosensitive material when frequency of incident radiation is increased by 30%, kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons increases from 0.4 eV. The work function of the surface is ______.
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1.3 eV and 2.8 eV respectively, successfully illuminate a metallic surface whose work function is 0.8 eV. The ratio of maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be ______.
Give Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?
