Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
उत्तर
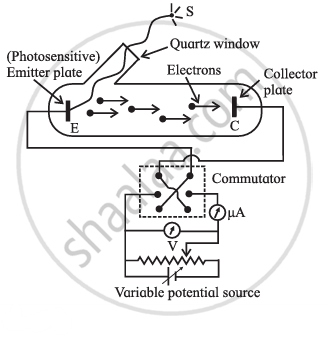 |
| Schematic of experimental set-up for photoelectric effect |
The experimental circuit to study the photoelectric effect is as shown in the figure.
It consists of an evacuated glass tube with a quartz window containing two photosensitive metal plates. One is the emitter E and another plate is the collector C.
The emitter and collector are connected to a voltage source whose voltage can be changed, and an ammeter is used to measure current.
A potential difference between E and C is measured by a voltmeter. Generally, C (anode) is at a positive terminal with respect to emitter E. When the anode potential (V) is positive, it accelerates the electrons. This potential is called accelerating potential. When the anode potential (V) is negative, it retards the flow of electrons. This potential is known as retarding potential. A source S of monochromahc light of sufficiently high frequency (λ ≤ 10 − 7) is used.
The applied P.D. between the plates can be changed with the help of potential divider arrangements by using a commulator key.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive material is doubled, then the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron will be ______.
Photocurrent recorded in the microammeter in an experimental setup of the photoelectric effect vanishes when the retarding potential is more than 0.8 V if the wavelength of incident radiation is 4950 Å. If the source of incident radiation is changed, the stopping potential turns out to be 1.2 V. Find the work function of the cathode material and the wavelength of the second source.
As the intensity of incident light increases ______
Find the energy of photon which have momentum 2 × 10-16 gm-cm/sec.
Explain the concept of the photoelectric effect.
If the total energy of radiation of frequency 1014 Hz is 6.63 J, Calculate the number of photons in the radiation.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
The work function of a surface is 3.1 eV. A photon of frequency 1 × 1015 Hz. Is an incident on it. Calculate the incident wavelength is photoelectric emission occurs or not.
With the help of a circuit diagram describe the experiment to study the characteristics of the photoelectric effect. Hence discuss any 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect.
When a light of wavelength 4000 Å falls on a photoelectric emitter, photoelectrons are liberated. For another emitter, light of wavelength 6000 Å is sufficient for photo emission. The work functions of the two emitters are in the ratio of ____________.
In photoelectric experiment, if both the intensity and frequency of the incident light are doubled, then the saturation of photoelectric current ______.
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
Photoelectrons are emitted from a photosensitive surface for the light of wavelengths λ1 = 360 nm and λ2 = 600 nm. What is the ratio of work functions for lights of wavelength 'λ1' to 'λ2'?
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
The radiations of energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV are incident on a metal surface having work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum velocities of the emitted photo-electrons is ____________.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons emitted from this surface have the de-Broglie wavelength '`lambda_1`' then ____________.
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
The ratio of slopes m1: ro2 of the lines given in the following graphs is, ______.
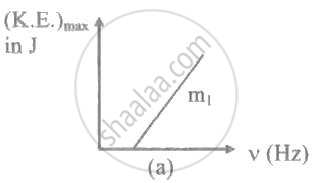
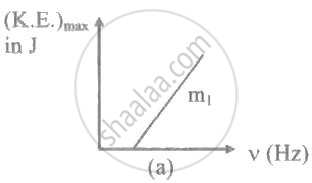
The stopping potential in the context of photoelectric effect depends on the following property of incident electromagnetic radiation ______.
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
We wish to observe an object which is 2.5Å in size. The minimum energy photon that can be used ______.
Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitive metallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons is ______.
If the electron in hydrogen atom jumps from second Bohr orbit to ground state and difference between energies of the two states is radiated in the form of photons. If the work function of the material is 4.2 eV, then stopping potential is ______.
[Energy of electron in nth orbit = `-13.6/"n"^2` eV ]
Light of wavelength λ, which is less than threshold wavelength is incident on a photosensitive material. If incident wavelength is decreased so that emitted photoelectrons are moving with same velocity, then stopping potential will ______.
When monochromatic light of frequency v1 falls on a metal surface, the stopping potential required is found to be V1. If the radiation of frequency v2 is incident on the surface, the stopping potential required V2 is ______. (v2 > v1)
