Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
Solution
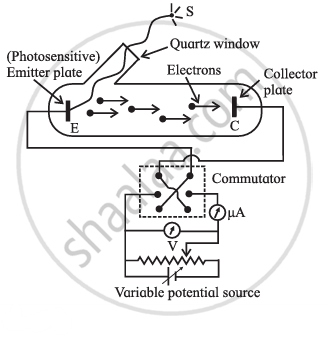 |
| Schematic of experimental set-up for photoelectric effect |
The experimental circuit to study the photoelectric effect is as shown in the figure.
It consists of an evacuated glass tube with a quartz window containing two photosensitive metal plates. One is the emitter E and another plate is the collector C.
The emitter and collector are connected to a voltage source whose voltage can be changed, and an ammeter is used to measure current.
A potential difference between E and C is measured by a voltmeter. Generally, C (anode) is at a positive terminal with respect to emitter E. When the anode potential (V) is positive, it accelerates the electrons. This potential is called accelerating potential. When the anode potential (V) is negative, it retards the flow of electrons. This potential is known as retarding potential. A source S of monochromahc light of sufficiently high frequency (λ ≤ 10 − 7) is used.
The applied P.D. between the plates can be changed with the help of potential divider arrangements by using a commulator key.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
Can microwaves be used in the experiment on photoelectric effect?
Explain the inverse linear dependence of stopping potential on the incident wavelength in a photoelectric effect experiment.
The electrons are emitted in the photoelectric effect from a metal surface.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a schematic of the experimental setup for the photoelectric effect.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
The energy of the incident photon on the metal surface is 3 W and then 5 W, where W is the work function for that metal. The ratio of velocities of emitted photoelectrons is ______.
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
When light falls on a metal surface, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons depends upon ______
For photoelectric emission from certain metal, the cut-off frequency is v. If radiation of frequency 2v impinges on the metal plate, the maximum possible velocity of the emitted electron will be (m is the electron mass) ____________.
The work function of a metal is 1.6 x 10-19 J. When the metal surface is illuminated by the light of wavelength 6400 Å, then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo-electrons will be (Planck's constant h = 6.4 x 10-34 Js) ____________.
Photoelectrons emitted from a metallic surface are initially ____________.
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photoemission, the wavelength of the incident light must be ______.
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (F) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph (v0 = Threshold frequency).
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ______.
Which one of the following statements ts INCORRECT for stopping potential in photoelectric emission?
When light of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on photosensitive surface, photons of power 'P' are emitted. The number of photons (n) emitted in 't' second is (h = Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in vacuum) ____________.
In a photoelectric experiment, ultraviolet light of wavelength 280 nm is used with a lithium cathode having work function Φ = 2.5 eV. If the wavelength of incident light is switched to 400 nm, find out the change in the stopping potential.
(h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js, c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
Photoelectrons are observed to just emit out of a material surface when the light of 620 nm falls on it with the intensity of 100 W m-2. If the light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the same material with an intensity of 1 W m-2, what would be the minimum reverse potential needed to stop the outflow of the electrons?
In a photocell, frequency of incident radiation is increased by keeping other factors constant (v > v0), the stopping potential ______.
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Give Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of photo-current as a function of accelerating potential for fixed incident intensity but different incident frequencies for the same emitter material.
