Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a schematic of the experimental setup for the photoelectric effect.
Solution

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
Given the following data for incident wavelength and the stopping potential obtained from an experiment on the photoelectric effect, estimate the value of Planck's constant and the work function of the cathode material. What is the threshold frequency and corresponding wavelength? What is the most likely metal used for emitter?
| Incident wavelength (in Å) | 2536 | 3650 |
| Stopping potential (in V) |
1.95 | 0.5 |
As the intensity of incident light increases ______
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
The minimum frequency for photoelectric effect on metal is 7 × 1014 Hz, Find the work function of the metal.
If the total energy of radiation of frequency 1014 Hz is 6.63 J, Calculate the number of photons in the radiation.
The kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectron emitted from a metal surface is doubled when the wavelength of the incident radiation is reduced from λ1 to λ2. The work function of the metal is ______
When light falls on a metal surface, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons depends upon ______
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
For photoelectric emission from certain metal, the cut-off frequency is v. If radiation of frequency 2v impinges on the metal plate, the maximum possible velocity of the emitted electron will be (m is the electron mass) ____________.
Threshold frequency for a metal is 1015 Hz. Light of `lambda` = 4000 Å falls on its surface. Which of the following statements is correct?
In photoelectric experiment, if both the intensity and frequency of the incident light are doubled, then the saturation of photoelectric current ______.
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
When certain metal surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength A., the stopping potential is V, When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is `("V"/3)`. The threshold wavelength for the surface is ______.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
Which one of the following statements ts INCORRECT for stopping potential in photoelectric emission?
The radiations of energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV are incident on a metal surface having work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum velocities of the emitted photo-electrons is ____________.
A light of wavelength '`lambda`' and intensity 'I' falls on photosensitive material. If 'N' photoelectrons are emitted, each with kinetic energy E, then ____________.
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength '`lambda`', the stopping potential for photoelectric effect is '3V0'. If the same surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength '`2 lambda`', the stopping potential is found as 'V0'. The threshold wavelength for this surface is ____________.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
The stopping potential in the context of photoelectric effect depends on the following property of incident electromagnetic radiation ______.
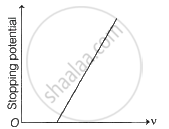
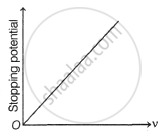
The following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (ν) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph [ν0 = threshold frequency].
|
(A) |
(B) |
|
(C) |
(D) |
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1.3 eV and 2.8 eV respectively, successfully illuminate a metallic surface whose work function is 0.8 eV. The ratio of maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be ______.
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies ν1 and ν2 of the incident light rays (ν1 > ν2). If the ratio of the maximum value of the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the first case to that in the second case is 2 : K, then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is ______.
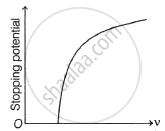
Draw a neat labelled diagram of photo-current as a function of accelerating potential for fixed incident intensity but different incident frequencies for the same emitter material.