Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
Options
potential
frequency
incident angle
pressure
Solution
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on frequency.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
It is observed in an experiment on the photoelectric effect that an increase in the intensity of the incident radiation does not change the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons. Where does the extra energy of the incident radiation go? Is it lost? State your answer with explanatory reasoning.
The electrons are emitted in the photoelectric effect from a metal surface.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
The work function of a surface is 3.1 eV. A photon of frequency 1 × 1015 Hz. Is an incident on it. Calculate the incident wavelength is photoelectric emission occurs or not.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
A metal surface is illuminated by light of given intensity and frequency to cause photoemission. If the intensity of illumination is reduced to one-fourth of its original value then the maximum KE of the emitted photoelectrons would be ______.
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
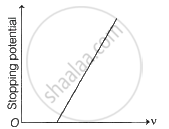
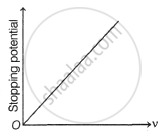
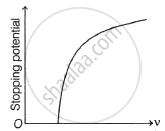
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (F) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph (v0 = Threshold frequency).
The work function of a photosensitive material is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photon emission from the substance is (approximately) ____________.
The radiations of energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV are incident on a metal surface having work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum velocities of the emitted photo-electrons is ____________.
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
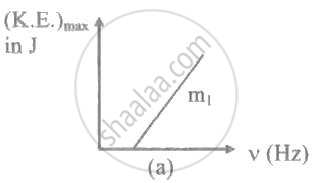
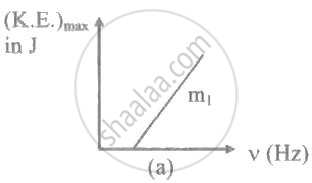
The ratio of slopes m1: ro2 of the lines given in the following graphs is, ______.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
Is it always necessary to use red light to get a photoelectric effect?
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected will be ______ eV when the light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. The work function of cesium = 1.9 eV.
We wish to observe an object which is 2.5Å in size. The minimum energy photon that can be used ______.
For a given photosensitive material and frequency (> threshold frequency) of incident radiation, the photoelectric current varies with the intensity of incident light as:
The following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (ν) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph [ν0 = threshold frequency].
|
(A) |
(B) |
|
(C) |
(D) |
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1.3 eV and 2.8 eV respectively, successfully illuminate a metallic surface whose work function is 0.8 eV. The ratio of maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be ______.
When monochromatic light of frequency v1 falls on a metal surface, the stopping potential required is found to be V1. If the radiation of frequency v2 is incident on the surface, the stopping potential required V2 is ______. (v2 > v1)
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Define photoelectric work function of a metal.
By increasing the voltage in an electron diffraction tube, the radius of the diffraction rings will ______.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.