Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Is it always necessary to use red light to get a photoelectric effect?
Solution
No, the broad wavelength and low energy of red light, photons do not have sufficient energy to pull an electron out of its orbital.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the photoelectric effect?
Explain the inverse linear dependence of stopping potential on the incident wavelength in a photoelectric effect experiment.
Radiation of wavelength 4500 Å is incident on a metal having work function 2.0 eV. Due to the presence of a magnetic field B, the most energetic photoelectrons emitted in a direction perpendicular to the field move along a circular path of radius 20 cm. What is the value of the magnetic field B?
Planck's constant is 6.6 × 10-34 Js. The momentum of each photon is given radiation Is 3.3 × 10-29 kg/s. The λ of radiation is ______.
Find the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, if in photoelectric effect energy of incident Photon is 4 eV and work function is 2.4 eV.
Find the energy of photon which have momentum 2 × 10-16 gm-cm/sec.
With the help of a circuit diagram describing an experiment to study the photoelectric effect.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
With the help of a circuit diagram describe the experiment to study the characteristics of the photoelectric effect. Hence discuss any 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect.
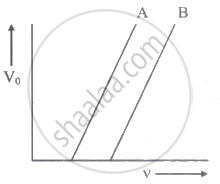
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in photoelectric effect is 3.2 × 10-19 J and the work-function for metal is 6.63 × 10-19 J, then stopping potential and threshold wavelength respectively are
[Planck's constant, h = 6.63 × 1034 J-s]
[Velocity of light, c = 3 × 108 `"m"/"s"`]
[Charge on electron= 1.6 × 10-19 C]
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
Light of different frequencies, whose photons have energies 3 eV and 18 eV respectively, successively illuminate a metal of work function 2 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons will be ______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ____________.
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (F) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph (v0 = Threshold frequency).
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ______.
A light of wavelength '`lambda`' and intensity 'I' falls on photosensitive material. If 'N' photoelectrons are emitted, each with kinetic energy E, then ____________.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons emitted from this surface have the de-Broglie wavelength '`lambda_1`' then ____________.
When light of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on photosensitive surface, photons of power 'P' are emitted. The number of photons (n) emitted in 't' second is (h = Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in vacuum) ____________.
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
The wavelength of light incident on a metal surface is reduced from 300 nm to 200 nm (both are less than threshold wavelength). What is the change in the stopping potential for photoelectrons emitted from the surface will be ______ V. (Take h = 6.6 × 10-34 J-s)
In a photocell, frequency of incident radiation is increased by keeping other factors constant (v > v0), the stopping potential ______.
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
