Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the photoelectric effect?
Solution
The phenomenon of emission of electrons from a metal surface when electromagnetic radiation of appropriate frequency is incident on it is known as photoelectric effect.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the inverse linear dependence of stopping potential on the incident wavelength in a photoelectric effect experiment.
It is observed in an experiment on the photoelectric effect that an increase in the intensity of the incident radiation does not change the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons. Where does the extra energy of the incident radiation go? Is it lost? State your answer with explanatory reasoning.
The threshold wavelength of tungsten is 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(a) Explain why no photoelectrons are emitted when the wavelength is more than 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(b) What will be the maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected in each of the following cases
(i) if ultraviolet radiation of wavelength λ = 1.80 × 10-5 cm and
(ii) radiation of frequency 4 x 1015 Hz is made incident on the tungsten surface?
Given the following data for incident wavelength and the stopping potential obtained from an experiment on the photoelectric effect, estimate the value of Planck's constant and the work function of the cathode material. What is the threshold frequency and corresponding wavelength? What is the most likely metal used for emitter?
| Incident wavelength (in Å) | 2536 | 3650 |
| Stopping potential (in V) |
1.95 | 0.5 |
As the intensity of incident light increases ______
Find the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, if in photoelectric effect energy of incident Photon is 4 eV and work function is 2.4 eV.
If the total energy of radiation of frequency 1014 Hz is 6.63 J, Calculate the number of photons in the radiation.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
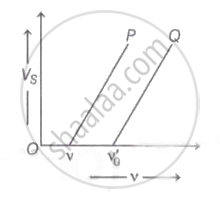
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in photoelectric effect is 3.2 × 10-19 J and the work-function for metal is 6.63 × 10-19 J, then stopping potential and threshold wavelength respectively are
[Planck's constant, h = 6.63 × 1034 J-s]
[Velocity of light, c = 3 × 108 `"m"/"s"`]
[Charge on electron= 1.6 × 10-19 C]
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
Photoelectrons emitted from a metallic surface are initially ____________.
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
When a surface 1 cm thick is illuminated by light of wavelength 'λ', the stopping potential is 'V0'. When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength '3λ', the stopping potential is `"V"_0/6`. The threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is ______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
A light of frequency 'v' is incident on the metal surface whose threshold frequency is 'v0'. If v = v0, then [c = speed of light in medium] ____________.
In experiment of photoelectric effect, the stopping potential for incident yellow light of wavelength 5890 Å is 4 volt. If the yellow light is replaced by blue light of wavelength 4000 Å, the stopping potential is ____________.
The stopping potential in the context of photoelectric effect depends on the following property of incident electromagnetic radiation ______.
In a photoelectric experiment, ultraviolet light of wavelength 280 nm is used with a lithium cathode having work function Φ = 2.5 eV. If the wavelength of incident light is switched to 400 nm, find out the change in the stopping potential.
(h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js, c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
We wish to observe an object which is 2.5Å in size. The minimum energy photon that can be used ______.
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1.3 eV and 2.8 eV respectively, successfully illuminate a metallic surface whose work function is 0.8 eV. The ratio of maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be ______.
When monochromatic light of frequency v1 falls on a metal surface, the stopping potential required is found to be V1. If the radiation of frequency v2 is incident on the surface, the stopping potential required V2 is ______. (v2 > v1)
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Explain the formation of clouds at high altitude.
