Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Can microwaves be used in the experiment on photoelectric effect?
Solution
No, using microwaves in the photoelectric effect experiment is not possible.
The microwave frequency is in the range of 109 Hz to 1012 Hz. This frequency range is insufficient to provide energy for the photoelectric effect.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the energy of photon which have momentum 2 × 10-16 gm-cm/sec.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a schematic of the experimental setup for the photoelectric effect.
Explain the concept of the photoelectric effect.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
With the help of a circuit diagram describe the experiment to study the characteristics of the photoelectric effect. Hence discuss any 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect.
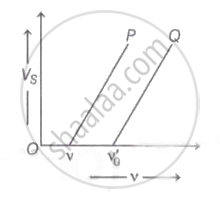
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
For photoelectric emission from certain metal, the cut-off frequency is v. If radiation of frequency 2v impinges on the metal plate, the maximum possible velocity of the emitted electron will be (m is the electron mass) ____________.
A metal surface is illuminated by light of given intensity and frequency to cause photoemission. If the intensity of illumination is reduced to one-fourth of its original value then the maximum KE of the emitted photoelectrons would be ______.
The work function of a metallic surface is 5.01 eV. The photoelectrons are emitted when light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on it. The potential difference applied to stop the fastest photoelectrons is [h = 4.14 x 10-15 eV sec] ____________.
In photoelectric experiment, if both the intensity and frequency of the incident light are doubled, then the saturation of photoelectric current ______.
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
Light of different frequencies, whose photons have energies 3 eV and 18 eV respectively, successively illuminate a metal of work function 2 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons will be ______.
The work function of a photosensitive material is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photon emission from the substance is (approximately) ____________.
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength '`lambda`', the stopping potential for photoelectric effect is '3V0'. If the same surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength '`2 lambda`', the stopping potential is found as 'V0'. The threshold wavelength for this surface is ____________.
When a metal with work function 0.6 eV is illuminated with light of energy 2 eV, the stopping potential will be ____________.
In a photoelectric experiment, ultraviolet light of wavelength 280 nm is used with a lithium cathode having work function Φ = 2.5 eV. If the wavelength of incident light is switched to 400 nm, find out the change in the stopping potential.
(h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js, c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
The radiation emitted, when an electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 orbit is a hydrogen atom, falls on a metal to produce photoelectron. The electrons from the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy are made to move perpendicular to a magnetic field of `1/320`T in a radius of 10-3m. Find the 320 work function of metal:
For a given photosensitive material and frequency (> threshold frequency) of incident radiation, the photoelectric current varies with the intensity of incident light as:
Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitive metallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons is ______.
In a photocell, frequency of incident radiation is increased by keeping other factors constant (v > v0), the stopping potential ______.
Light of wavelength λ, which is less than threshold wavelength is incident on a photosensitive material. If incident wavelength is decreased so that emitted photoelectrons are moving with same velocity, then stopping potential will ______.
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1.3 eV and 2.8 eV respectively, successfully illuminate a metallic surface whose work function is 0.8 eV. The ratio of maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be ______.
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies ν1 and ν2 of the incident light rays (ν1 > ν2). If the ratio of the maximum value of the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the first case to that in the second case is 2 : K, then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is ______.
