Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can microwaves be used in the experiment on photoelectric effect?
उत्तर
No, using microwaves in the photoelectric effect experiment is not possible.
The microwave frequency is in the range of 109 Hz to 1012 Hz. This frequency range is insufficient to provide energy for the photoelectric effect.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is it always possible to see the photoelectric effect with a red light?
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
If the total energy of radiation of frequency 1014 Hz is 6.63 J, Calculate the number of photons in the radiation.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
With the help of a circuit diagram describing an experiment to study the photoelectric effect.
State Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain all characteristics of the photoelectric effect, on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photoemission, the wavelength of the incident light must be ______.
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
Light of different frequencies, whose photons have energies 3 eV and 18 eV respectively, successively illuminate a metal of work function 2 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons will be ______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
Which one of the following statements ts INCORRECT for stopping potential in photoelectric emission?
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
When light of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on photosensitive surface, photons of power 'P' are emitted. The number of photons (n) emitted in 't' second is (h = Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in vacuum) ____________.
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
The wavelength of light incident on a metal surface is reduced from 300 nm to 200 nm (both are less than threshold wavelength). What is the change in the stopping potential for photoelectrons emitted from the surface will be ______ V. (Take h = 6.6 × 10-34 J-s)
We wish to observe an object which is 2.5Å in size. The minimum energy photon that can be used ______.
A point isotropic light source of power P = 12 watts is located on the axis of a circular mirror of radius R = 3 cm. If the distance of the source from the centre of the mirror is a = 39 cm and the reflection coefficient of the mirror is α = 0.70 then the force exerted by the light ray on the mirror is ______ × 10-10 N.
A charged dust particle of radius 5 × 10-7 m is located in a horizontal electric field having an intensity of 6.28 × 105 V/m. The surrounding medium is air with a coefficient of viscosity η = 1.6 × 10-5 N-s/m2. If the particle moves with a uniform horizontal speed of 0.02 m/s, the number of electrons on it is ______.
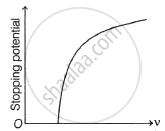
For a given photosensitive material and frequency (> threshold frequency) of incident radiation, the photoelectric current varies with the intensity of incident light as:
In a photocell, frequency of incident radiation is increased by keeping other factors constant (v > v0), the stopping potential ______.
If the electron in hydrogen atom jumps from second Bohr orbit to ground state and difference between energies of the two states is radiated in the form of photons. If the work function of the material is 4.2 eV, then stopping potential is ______.
[Energy of electron in nth orbit = `-13.6/"n"^2` eV ]
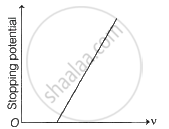
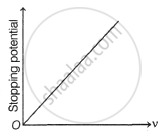
The following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (ν) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph [ν0 = threshold frequency].
|
(A) |
(B) |
|
(C) |
(D) |
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of photo-current as a function of accelerating potential for fixed incident intensity but different incident frequencies for the same emitter material.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?