Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a circuit diagram describing an experiment to study the photoelectric effect.
उत्तर
- A laboratory experimental set-up for the photoelectric effect consists of an evacuated glass tube with a quartz window.
- The glass tube contains photosensitive metal plates. One is the emitter E and another plate is the collector C.

Schematic of experimental set-up for the photoelectric effect - The emitter and collector are connected to a voltage source whose voltage can be changed and to an ammeter to measure the current in the circuit.
- A potential difference of V, as measured by the voltmeter, is maintained between the emitter E and collector C. Generally, C (the anode) is at a positive potential with respect to the emitter E (the cathode). This potential difference can be varied and C can even be at a negative potential with respect to E.
- When the anode potential (V) is positive, it accelerates the electrons. This potential is called accelerating potential. When the anode potential (V) is negative, it retards the flow of electrons. This potential is known as retarding potential.
- A source S of monochromatic light of sufficiently high frequency (short wavelength ≤ 10–7 m) is used.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can microwaves be used in the experiment on photoelectric effect?
Explain the inverse linear dependence of stopping potential on the incident wavelength in a photoelectric effect experiment.
Given the following data for incident wavelength and the stopping potential obtained from an experiment on the photoelectric effect, estimate the value of Planck's constant and the work function of the cathode material. What is the threshold frequency and corresponding wavelength? What is the most likely metal used for emitter?
| Incident wavelength (in Å) | 2536 | 3650 |
| Stopping potential (in V) |
1.95 | 0.5 |
Planck's constant is 6.6 × 10-34 Js. The momentum of each photon is given radiation Is 3.3 × 10-29 kg/s. The λ of radiation is ______.
Define photoelectric effect.
Find the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, if in photoelectric effect energy of incident Photon is 4 eV and work function is 2.4 eV.
With the help of a circuit diagram describe the experiment to study the characteristics of the photoelectric effect. Hence discuss any 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is v. Charge and the mass of the photoelectron is denoted by e and m, respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
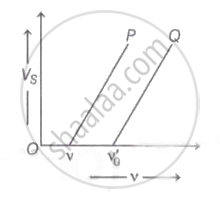
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
Threshold frequency for a metal is 1015 Hz. Light of `lambda` = 4000 Å falls on its surface. Which of the following statements is correct?
The work function of a metal is 1.6 x 10-19 J. When the metal surface is illuminated by the light of wavelength 6400 Å, then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo-electrons will be (Planck's constant h = 6.4 x 10-34 Js) ____________.
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength '`lambda`', the stopping potential for photoelectric effect is '3V0'. If the same surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength '`2 lambda`', the stopping potential is found as 'V0'. The threshold wavelength for this surface is ____________.
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
A light of frequency 'v' is incident on the metal surface whose threshold frequency is 'v0'. If v = v0, then [c = speed of light in medium] ____________.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
The following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (ν) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph [ν0 = threshold frequency].
|
(A) |
(B) |
|
(C) |
(D) |
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies ν1 and ν2 of the incident light rays (ν1 > ν2). If the ratio of the maximum value of the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the first case to that in the second case is 2 : K, then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is ______.
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Explain the formation of clouds at high altitude.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?