Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
Solution
- The phenomenon of emission of electrons from a metal surface, when radiation of appropriate frequency is incident on it, is known as the photoelectric effect.
- If increasingly negative potentials were applied to the collector in the experiment of the photoelectric effect, the photocurrent decreases and for some typical value (– V0), photocurrent becomes zero. This value of V0 is termed as cut-off or stopping potential.
- The minimum amount of energy required to be provided to an electron to pull it out of the metal from the surface is called the work function of the metal.
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive material is doubled, then the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron will be ______.
Photocurrent recorded in the microammeter in an experimental setup of the photoelectric effect vanishes when the retarding potential is more than 0.8 V if the wavelength of incident radiation is 4950 Å. If the source of incident radiation is changed, the stopping potential turns out to be 1.2 V. Find the work function of the cathode material and the wavelength of the second source.
Radiation of wavelength 4500 Å is incident on a metal having work function 2.0 eV. Due to the presence of a magnetic field B, the most energetic photoelectrons emitted in a direction perpendicular to the field move along a circular path of radius 20 cm. What is the value of the magnetic field B?
As the intensity of incident light increases ______
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
The energy of a photon is 2 eV. Find its frequency and wavelength.
The energy of the incident photon on the metal surface is 3 W and then 5 W, where W is the work function for that metal. The ratio of velocities of emitted photoelectrons is ______.
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
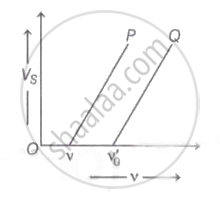
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photoemission, the wavelength of the incident light must be ______.
The threshold frequency for a certain photosensitive metal is v0. When it is illuminated by light of frequency v = 2v0, the maximum velocity of photoelectrons is v0. What will be the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons when the same metal is illuminated by light of frequency
v = 5v0?
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
When a surface 1 cm thick is illuminated by light of wavelength 'λ', the stopping potential is 'V0'. When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength '3λ', the stopping potential is `"V"_0/6`. The threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is ______.
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ____________.
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ______.
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength '`lambda`', the stopping potential for photoelectric effect is '3V0'. If the same surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength '`2 lambda`', the stopping potential is found as 'V0'. The threshold wavelength for this surface is ____________.
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
In experiment of photoelectric effect, the stopping potential for incident yellow light of wavelength 5890 Å is 4 volt. If the yellow light is replaced by blue light of wavelength 4000 Å, the stopping potential is ____________.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
Which one of the following graphs represents the variation of photoelectric current (i) with intensity (I) of the incident light?
In a photoelectric experiment, ultraviolet light of wavelength 280 nm is used with a lithium cathode having work function Φ = 2.5 eV. If the wavelength of incident light is switched to 400 nm, find out the change in the stopping potential.
(h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js, c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
The radiation emitted, when an electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 orbit is a hydrogen atom, falls on a metal to produce photoelectron. The electrons from the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy are made to move perpendicular to a magnetic field of `1/320`T in a radius of 10-3m. Find the 320 work function of metal:
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies ν1 and ν2 of the incident light rays (ν1 > ν2). If the ratio of the maximum value of the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the first case to that in the second case is 2 : K, then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is ______.
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Explain the formation of clouds at high altitude.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
