Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The energy of a photon is 2 eV. Find its frequency and wavelength.
Solution
Given:
E = 2 eV = 2 × 1.6 × 10−19 = 3.2 × 10−19 J
To find:
- Frequency (ν)
- Wavelength (λ)
Formulae:
- E = hν
- λ = `c/ν`
Calculation:
i. Using formula (i),
v = `(3.2 xx 10^-19)/(6.63 xx 10^-34)`
= `(3.2 xx 10^15)/6.63`
= antilog {log (3.2) + log(1015) − log(6.63)}
= antilog {0.5051 + 15 − 0.8215}
= antilog {14.6836}
= 4.826 × 1014 Hz
The frequency of photons is 4.826 × 1014 Hz.
ii. Using formula (ii),
`λ = c/ν = (3 xx 10^8)/(4.826 xx 10^14)`
= antilog {log 3 − log 4.826} × 10−6
= antilog {0.4771 − 0.6836} × 10−6
= antilog {`overline1`.7935} × 10−6
= 0.6216 × 10−6m
= 6216 × 10−5 m
= 6216 Å
The wavelength of the photon is 6216 Å.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Is it always possible to see the photoelectric effect with a red light?
Explain the inverse linear dependence of stopping potential on the incident wavelength in a photoelectric effect experiment.
Find the energy of photon which have momentum 2 × 10-16 gm-cm/sec.
State Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain all characteristics of the photoelectric effect, on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is v. Charge and the mass of the photoelectron is denoted by e and m, respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
The maximum velocity of photoelectron emitted is 4.8 m/s. If the e/m ratio of the electron is 1.76 × 1011 C/kg, then stopping potential is given by ______
The kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectron emitted from a metal surface is doubled when the wavelength of the incident radiation is reduced from λ1 to λ2. The work function of the metal is ______
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
An important spectral emission line has a wavelength of 21 cm. The corresponding photon energy is (h = 6.62 x 10-34 Js, c = 3 x 108 m/s) ____________.
The threshold frequency for a certain photosensitive metal is v0. When it is illuminated by light of frequency v = 2v0, the maximum velocity of photoelectrons is v0. What will be the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons when the same metal is illuminated by light of frequency
v = 5v0?
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ____________.
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (F) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph (v0 = Threshold frequency).
A metal surface having work function 'w0' emits photoelectrons when photons of energy 'E' are incident on it. The electron enters the uniform magnetic field (B) in perpendicular direction and moves in circular path of radius 'r'. Then 'r' is equal to (m and e be the mass and charge of electron respectively) ____________.
The ratio of slopes m1: ro2 of the lines given in the following graphs is, ______.
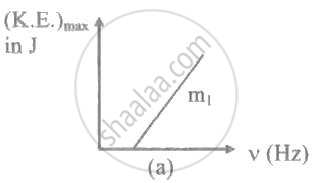
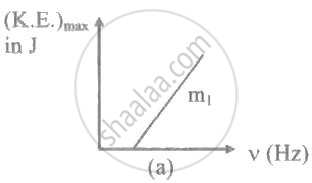
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
Photoelectrons are observed to just emit out of a material surface when the light of 620 nm falls on it with the intensity of 100 W m-2. If the light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the same material with an intensity of 1 W m-2, what would be the minimum reverse potential needed to stop the outflow of the electrons?
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected will be ______ eV when the light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. The work function of cesium = 1.9 eV.
On a photosensitive material when frequency of incident radiation is increased by 30%, kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons increases from 0.4 eV. The work function of the surface is ______.
Light of wavelength λ, which is less than threshold wavelength is incident on a photosensitive material. If incident wavelength is decreased so that emitted photoelectrons are moving with same velocity, then stopping potential will ______.
When monochromatic light of frequency v1 falls on a metal surface, the stopping potential required is found to be V1. If the radiation of frequency v2 is incident on the surface, the stopping potential required V2 is ______. (v2 > v1)
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Give Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
In a photoelectric experiment, the stopping potential is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron?
