Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the concept of the photoelectric effect.
Solution
- The phenomenon of emission of electrons from a metal surface, when radiation of appropriate frequency is incident on it, is known as the photoelectric effect.
- The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons and the resulting current in the circuit due to them is called photoelectric current.
- When ultraviolet radiations fall on the emitter plate, electrons are ejected from it.
- They are attracted towards the positive collector plate by the electric field. Thus, light falling on the surface of the emitter causes a current in the external circuit.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the total energy of radiation of frequency 1014 Hz is 6.63 J, Calculate the number of photons in the radiation.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
What is the photoelectric effect? Define stopping potential and photoelectric work function.
The work function of a surface is 3.1 eV. A photon of frequency 1 × 1015 Hz. Is an incident on it. Calculate the incident wavelength is photoelectric emission occurs or not.
The ratio of energies of photons produced due to transition of electron of hydrogen atom from its (i) second to first energy level and (ii) highest energy level to second level is respectively.
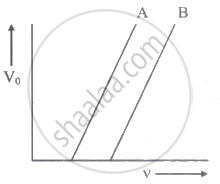
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
When light falls on a metal surface, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons depends upon ______
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
The work function of a metal is 1.6 x 10-19 J. When the metal surface is illuminated by the light of wavelength 6400 Å, then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo-electrons will be (Planck's constant h = 6.4 x 10-34 Js) ____________.
In photoelectric experiment, if both the intensity and frequency of the incident light are doubled, then the saturation of photoelectric current ______.
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photoemission, the wavelength of the incident light must be ______.
In photoelectric effect, for a light of different intensities but of same frequency, the stopping potential for a given metal is ____________.
When certain metal surface is illuminated with a light of wavelength A., the stopping potential is V, When the same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is `("V"/3)`. The threshold wavelength for the surface is ______.
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ____________.
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ______.
Is it always necessary to use red light to get a photoelectric effect?
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
A charged dust particle of radius 5 × 10-7 m is located in a horizontal electric field having an intensity of 6.28 × 105 V/m. The surrounding medium is air with a coefficient of viscosity η = 1.6 × 10-5 N-s/m2. If the particle moves with a uniform horizontal speed of 0.02 m/s, the number of electrons on it is ______.
On a photosensitive material when frequency of incident radiation is increased by 30%, kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons increases from 0.4 eV. The work function of the surface is ______.
Light of wavelength λ, which is less than threshold wavelength is incident on a photosensitive material. If incident wavelength is decreased so that emitted photoelectrons are moving with same velocity, then stopping potential will ______.
The photoelectric threshold for a certain metal surface is 3600 Å. If the metal surface is irradiated by a wavelength of 1100 Å, then kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is ______.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of photo-current as a function of accelerating potential for fixed incident intensity but different incident frequencies for the same emitter material.
The threshold frequency for a certain metal for photoelectric effect is 1.7 x 1015 Hz. When a light of frequency 2.2 x 1015 Hz is incident on the metal surface, the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is 3.3 x.10-19 J. Calculate Planck's constant.
