Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The threshold wavelength of tungsten is 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(a) Explain why no photoelectrons are emitted when the wavelength is more than 2.76 x 10-5 cm.
(b) What will be the maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected in each of the following cases
(i) if ultraviolet radiation of wavelength λ = 1.80 × 10-5 cm and
(ii) radiation of frequency 4 x 1015 Hz is made incident on the tungsten surface?
Solution
Data: λ0 = 2.76 x 10-5 cm = 2.76 x 10-7 m,
λ = 1.80 × 10-5 cm = 1.80 × 10-7 m,
v = 4 × 1015 Hz,
h = 6.63 × 10-34 J.s,
c = 3 × 108 m/s
(a) For λ > λ0,v < v0 (threshold frequency).
∴ hv < hv0. Hence, no photoelectrons are emitted.
(b) Maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected
`= "hc" (1/lambda - 1/lambda_0)`
`= (6.63 xx 10^-34)(3 xx 10^8)(10^7/1.8 - 10^7/2.76)`J
= (6.63 × 10-19)(3)(0.5555 - 0.3623)
= (6.63)(3)(0.1932 × 10-19)J
= 3.842 × 10-19J
`= (3.842 xx 10^-19 "J")/(1.6 xx 10^-19 "J"//"eV")`
= 2.40 eV
(c) Maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected
= hv - `"hc"/lambda_0`
`= (6.63 xx 10^-34)(4 xx 10^15) - ((6.63 xx 10^-34)(3 xx 10^8))/(2.76 xx 10^-7)`
= 26.52 × 10-19 - 7.207 × 10-19
= 19.313 × 10-19 J
= `(19.313 xx 10^19 "J")/(1.6 xx 10^-19 "J"//"eV")`
= 12.07 eV
RELATED QUESTIONS
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
Radiation of wavelength 4500 Å is incident on a metal having work function 2.0 eV. Due to the presence of a magnetic field B, the most energetic photoelectrons emitted in a direction perpendicular to the field move along a circular path of radius 20 cm. What is the value of the magnetic field B?
The electrons are emitted in the photoelectric effect from a metal surface.
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a schematic of the experimental setup for the photoelectric effect.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is v. Charge and the mass of the photoelectron is denoted by e and m, respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
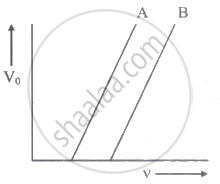
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
When a photon enters glass from air, which one of the following quantity does not change?
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
The work function of a metal is 1.6 x 10-19 J. When the metal surface is illuminated by the light of wavelength 6400 Å, then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo-electrons will be (Planck's constant h = 6.4 x 10-34 Js) ____________.
Photoelectrons emitted from a metallic surface are initially ____________.
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photoemission, the wavelength of the incident light must be ______.
When wavelength of incident radiation on the metal surface is reduced from 'λ1' to 'λ2', the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons is tripled. The work function of the metal is ______.
(h = Planck's constant, c =velocity of light)
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
When a metal with work function 0.6 eV is illuminated with light of energy 2 eV, the stopping potential will be ____________.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons emitted from this surface have the de-Broglie wavelength '`lambda_1`' then ____________.
When light of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on photosensitive surface, photons of power 'P' are emitted. The number of photons (n) emitted in 't' second is (h = Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in vacuum) ____________.
In experiment of photoelectric effect, the stopping potential for incident yellow light of wavelength 5890 Å is 4 volt. If the yellow light is replaced by blue light of wavelength 4000 Å, the stopping potential is ____________.
The radiation corresponding to the 3 → 2 transition of a hydrogen atom falls on a gold surface to generate photoelectrons. These electrons are passed through a magnetic field of 5 × 10-4 T. Assume that the radius of the largest circular path followed by these electrons is 7 mm, and the work function of the metal is ______.
(Mass of electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg)
The stopping potential in the context of photoelectric effect depends on the following property of incident electromagnetic radiation ______.
The radiation emitted, when an electron jumps from n = 3 to n = 2 orbit is a hydrogen atom, falls on a metal to produce photoelectron. The electrons from the metal surface with maximum kinetic energy are made to move perpendicular to a magnetic field of `1/320`T in a radius of 10-3m. Find the 320 work function of metal:
We wish to observe an object which is 2.5Å in size. The minimum energy photon that can be used ______.
A charged dust particle of radius 5 × 10-7 m is located in a horizontal electric field having an intensity of 6.28 × 105 V/m. The surrounding medium is air with a coefficient of viscosity η = 1.6 × 10-5 N-s/m2. If the particle moves with a uniform horizontal speed of 0.02 m/s, the number of electrons on it is ______.
When monochromatic light of frequency v1 falls on a metal surface, the stopping potential required is found to be V1. If the radiation of frequency v2 is incident on the surface, the stopping potential required V2 is ______. (v2 > v1)
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in the photoelectric effect is 2eV, the stopping potential will be ______.
Explain the experimental set-up of photoelectric effect.
