Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are made of circular discs of radii 5⋅0 cm each. If the separation between the plates is 1⋅0 mm, what is the capacitance?
उत्तर
The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is given by `C = (∈_0A)/d`
Here ,
A = Area of the plate
d = Distance between the parallel plates
Given :
`A = pir^2 = pi xx (5 xx 10^-2)^2`
`d = 1.0 xx 10^-3 "m"`
`∈_0 = 8.85 xx 10^-12 F/m`
`therefore C = (∈_0A)/d`
= `(8.85 xx 10^-12 xx 3.14 xx 25 xx 10^-4)/10^-3`
= `6.95 xx 10^-5 uF`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
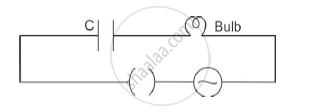
A bulb is connected in series with a variable capacitor and an AC source as shown. What happens to the brightness of the bulb when the key is plugged in and capacitance of the capacitor is gradually reduced?
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential V. It is then connected to another uncharged capacitor having the same capacitance. Find out the ratio of the energy stored in the combined system to that stored initially in the single capacitor.
A capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential V. The flux of the electric field through a closed surface enclosing the capacitor is
Two metal spheres of capacitance C1 and C2 carry some charges. They are put in contact and then separated. The final charges Q1 and Q2 on them will satisfy
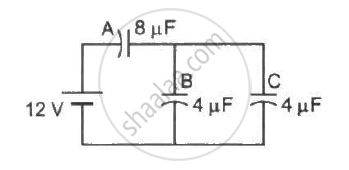
Find the charge appearing on each of the three capacitors shown in figure .
Two conducting spheres of radii R1 and R2 are kept widely separated from each other. What are their individual capacitances? If the spheres are connected by a metal wire, what will be the capacitance of the combination? Think in terms of series−parallel connections.
A cylindrical capacitor is constructed using two coaxial cylinders of the same length 10 cm and of radii 2 mm and 4 mm. (a) Calculate the capacitance. (b) Another capacitor of the same length is constructed with cylinders of radii 4 mm and 8 mm. Calculate the capacitance.
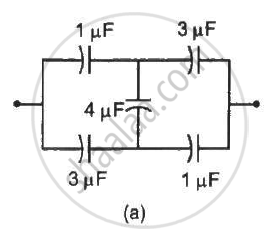
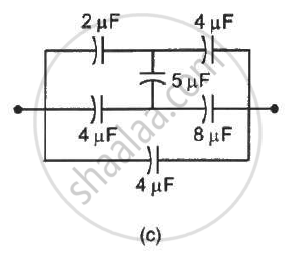
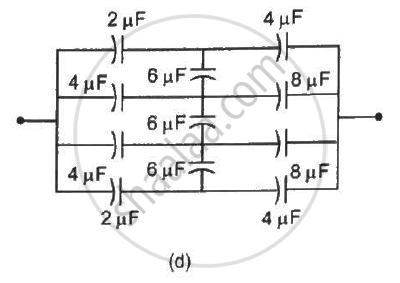
Find the equivalent capacitances of the combinations shown in figure between the indicated points.

A 5⋅0 µF capacitor is charged to 12 V. The positive plate of this capacitor is now connected to the negative terminal of a 12 V battery and vice versa. Calculate the heat developed in the connecting wires.
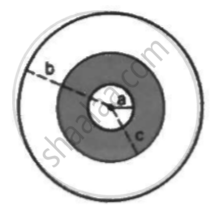
A sphercial capacitor is made of two conducting spherical shells of radii a and b. The space between the shells is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant K up to a radius c as shown in figure . Calculate the capacitance.
Obtain the expression for capacitance for a parallel plate capacitor.
Derive the expression for resultant capacitance, when the capacitor is connected in series.
The work done in placing a charge of 8 × 10–18 coulomb on a condenser of capacity 100 micro-farad is ______.
Three capacitors 2µF, 3µF, and 6µF are joined in series with each other. The equivalent capacitance is ____________.
Consider two conducting spheres of radii R1 and R2 with R1 > R2. If the two are at the same potential, the larger sphere has more charge than the smaller sphere. State whether the charge density of the smaller sphere is more or less than that of the larger one.
A parallel plate capacitor is filled by a dielectric whose relative permittivity varies with the applied voltage (U) as ε = αU where α = 2V–1. A similar capacitor with no dielectric is charged to U0 = 78V. It is then connected to the uncharged capacitor with the dielectric. Find the final voltage on the capacitors.
A leaky parallel plate capacitor is filled completely with a material having dielectric constant K = 5 and electric conductivity σ = 7.4 × 10-12 Ω-1 m-1. If the charge on the plate at the instant t = 0 is q = 8.85 µC, then the leakage current at the instant t = 12 s is ______ × 10-1 µA.
A capacitor with capacitance 5µF is charged to 5 µC. If the plates are pulled apart to reduce the capacitance to 2 µF, how much work is done?
