Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The sides of certain triangles are given below. Determine which of them right triangles are.
9cm, 16cm, 18cm
उत्तर
For the given triangle to be right-angled, the sum of the two sides must be equal to the square of the third side.
Here, let the three sides of the triangle be a, b and c.
a = 9 cm, b = 16 cm and c = 18 cm
`a^2+b^2=9^2+16^2`
=81+256
=337
`c^2=19^2`
=361
`a^2+b^2≠c^2`
Thus, the given triangle is not right-angled.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State which pair of triangles in the following figure are similar. Write the similarity criterion used by you for answering the question, and also write the pairs of similar triangles in the symbolic form:
In the following figure, altitudes AD and CE of ΔABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
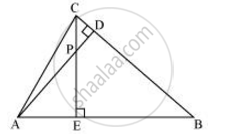
ΔAEP ∼ ΔCDP
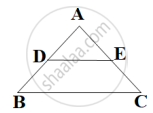
Sides AB and AC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ and PR and median PM of another triangle PQR. Show that ΔABC ~ ΔPQR.
The sides of certain triangles are given below. Determine which of them right triangles are.
(a – 1) cm, `2sqrta` cm, (a + 1) cm
In ABC, DE || AB. If CD = 3 cm, EC = 4 cm, BE = 6 cm, then DA is equal to ______.
In the figure, if DE∥BC, AD = 3cm, BD = 4cm and BC= 14 cm, then DE equals ______.
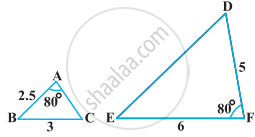
It is given that ∆ABC ~ ∆EDF such that AB = 5 cm, AC = 7 cm, DF = 15 cm and DE = 12 cm. Find the lengths of the remaining sides of the triangles.
In triangles ABC and DEF, ∠B = ∠E, ∠F = ∠C and AB = 3DE. Then, the two triangles are ______.
In figure, if ∠D = ∠C, then it is true that ΔADE ~ ΔACB? Why?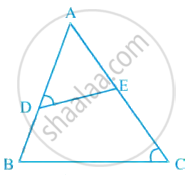
If ΔABC ~ ΔDEF and ∠A = 47°, ∠E = 83°, then ∠C is equal ______.
