Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The weight of an empty balloon on a spring balance is W1. The weight becomes W2when the balloon is filled with air. Let the weight of the air itself be w. Neglect the thickness of the balloon when it is filled with air. Also neglect the difference in the densities of air inside and outside the balloon.
(a) W2 = W1
(b) W2 = W1 + w
(c) W2 < W1 + w
(d) W2 > W1
उत्तर
(a) W2 = W1
(c) W2 < W1 + w
According to the question, the density of air inside and outside the balloon is the same. So, the weight w of air inside the balloon is equal to the weight of displaced air. Thus, the spring balance will not register any difference because the balloon will experience buoyant force equal to w that cancels out the weight of the added air.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A manometer reads the pressure of a gas in an enclosure as shown in Figure (a) When a pump removes some of the gas, the manometer reads as in Figure (b) The liquid used in the manometers is mercury and the atmospheric pressure is 76 cm of mercury.
(a) Give the absolute and gauge pressure of the gas in the enclosure for cases (a) and (b), in units of cm of mercury.
(b) How would the levels change in case (b) if 13.6 cm of water (immiscible with mercury) are poured into the right limb of the manometer? (Ignore the small change in the volume of the gas).

A one meter long glass tube is open at both ends. One end of the tube is dipped into a mercury cup, the tube is kept vertical and the air is pumped out of the tube by connecting the upper end to a suction pump. Can mercury be pulled up into the pump by this process?
A satellite revolves round the earth. Air pressure inside the satellite is maintained at 76 cm of mercury. What will be the height of mercury column in a barometer tube 1 m long placed in the satellite?
The three vessels shown in the following figure have same base area. Equal volumes of a liquid are poured in the three vessels. The force on the base will be
Equal mass of three liquids are kept in three identical cylindrical vessels A, B and C. The densities are ρA, ρB, ρC with ρA < ρB < ρC. The force on the base will be
Shows in the following figure a siphon. The liquid shown is water. The pressure difference PB − PAbetween the points A and B is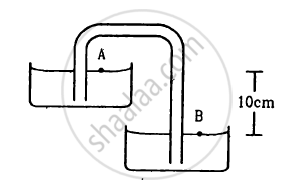
Suppose the pressure at the surface of mercury in a barometer tube is P1 and the pressure at the surface of mercury in the cup is P2.
A barometer kept in an elevator reads 76 cm when it is at rest. If the elevator goes up with increasing speed, the reading will be ______.
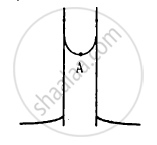
Figure shows a capillary tube of radius r dipped into water. If the atmospheric pressure is P0, the pressure at point A is
The surface of water in a water tank on the top of a house is 4 m above the tap level. Find the pressure of water at the tap when the tap is closed. Is it necessary to specify that the tap is closed?
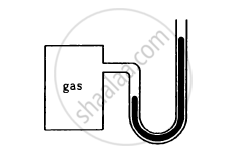
The heights of mercury surfaces in the two arms of the manometer shown in figure are 2 cm and 8 cm.
Atmospheric pressure = 1.01 × 105 N−2. Find (a) the pressure of the gas in the cylinder and (b) the pressure of mercury at the bottom of the U tube.
A closed vessel is half filled with water. There is a hole near the top of the vessel and air is pumped out from this hole.
(a) The water level will rise up in the vessel.
(b) The pressure at the surface of the water will decrease
(c) The force by the water on the bottom of the vessel will decrease
(d) The density of the liquid will decrease
Suppose the glass of the previous problem is covered by a jar and the air inside the jar is completely pumped out. (a) What will be the answers to the problem? (b) Show that the answers do not change if a glass of different shape is used provided the height, the bottom area and the volume are unchanged.
If water be used to construct a barometer, what would be the height of water column at standard atmospheric pressure (76 cm of mercury) ?
A U-tube containing a liquid is accelerated horizontally with a constant acceleration a0. If the separation between the vertical limbs is l, find the difference in the heights of the liquid in the two arms.
A glass capillary sealed at the upper end is of length 0.11 m and internal diameter 2 × 10-5 m. This tube is immersed vertically into a liquid of surface tension 5.06 × 10-2 N/m. When the length x × 10-2 m of the tube is immersed in liquid then the liquid level inside and outside the capillary tube becomes the same, then the value of x is ______ m. (Assume atmospheric pressure is 1.01 × 105 `"N"/"m"^2`)
